
Have you ever felt this way: some specific sounds, which are obviously not too loud, can make people feel uncomfortable, such as nails scratching the blackboard, eating and chicking, coughing and clearing the throat, typing and typing, rough breathing…
Why does the sound make people feel uncomfortable

Some people feel resistant to specific voices, and the main influencing factors are as follows.
1. The frequency range of sound
In general, the frequency of the sound that the human ear can recognize is between 20Hz and 20000Hz, which is called audible sound. The basic frequency of a person’s usual speaking voice is only between 80 Hz and 260 Hz.
2000Hz to 5000Hz is the most sensitive response range of the human ear. When the sound is in this range, it will be unpleasant. For example, nail scratching on blackboard, knife scraping glass, human screams, etc., all belong to this frequency range.
From a neurological point of view, the explanation is that the amygdala in the brain makes us feel uncomfortable. When the amygdala hears the sound of nails scratching the blackboard, etc., it will “craze” abnormally. As a result, he overbearingly took over the task of the brain’s hearing, sending painful messages to the auditory cortex.
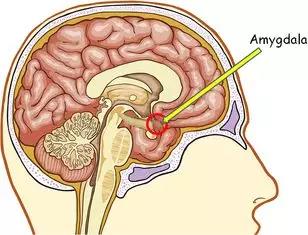
The pointing position of the arrow is the amygdala
Differences in human body’s physiological structure
There are differences in the sound frequency range and related physiological structure that people can accept. Even with “piercing voices”, everyone has different emotional reaction tendencies, tolerances and hearing thresholds.
For the same sound stimulation, some people are unbearable, some don’t feel too strong, and some people think of other specific scenes.
3. Phonophobia
Phonophobia is particularly sensitive to individual noises, which can be manifested as inability to tolerate certain sounds, such as eating, throat clearing, keyboard knocking, alarm clock, stainless steel container scraping, rough breathing and so on.
These may sound nothing to others, or even feel it, but for people with phonophobia, they can “direct the soul.”
They have negative emotions such as disgust, irritability, madness, or anxiety about certain sounds, and sometimes have a rapid heartbeat, a lot of sweating, and muscle cramps.
In addition, a new study published in the American journal Journal of Neuroscience shows that certain phonophobia is associated with enhanced “mirror behavior” in the brain: people with phonophobia feel that they are Imitate the mouth movements that can produce these trigger sounds. For example, chewing, swallowing, coughing, etc.
How sound affects health
Some sounds can make people feel irritable or disgusting, but other sounds can affect health.
The intensity of the sound is measured in decibels. Generally speaking, 30 decibels is a quiet room; 40 decibels is the sound of normal indoor communication; 70 decibels is the sound of a vacuum cleaner; 90 decibels is the sound of a motorcycle engine; 100 The decibel is equivalent to the sound of an electric drill during decoration; at 110 decibels, the human body will obviously feel unbearable.
If the sound is uncomfortable, it means that the sound source has caused noise pollution. As early as the end of 2011, the World Health Organization issued the Report on the Burden of Disease Caused by Noise Pollution, which believed that noise hazards were second only to air pollution.

Living in a noisy environment for a long time will bring these burdens to the body:
Hearing loss
Long-term, high-volume noise can cause hearing loss by damaging inner ear hair cells, spiral organs, auditory nerve fibers, and auditory neurons.

Sudden and violent noise can cause tympanic membrane damage, hearing loss, and noise-induced deafness; if the vestibular receptors in the ear are damaged, it can cause dizziness, vomiting, and unstable walking.
Continuous interference with sleep
Normally, continuous noise exceeding 40 decibels may “wake up” light-sleeping people, and sudden noise exceeding 60 decibels may awaken most people. Frequent disturbance of sleep by noise for a long time can cause neurasthenia and even depression.
Affect vascular health
Sustained noise interruption can increase the risk of high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke. The source of noise that the individual cannot control will become a kind of stress, causing the body to secrete adrenaline and other “stress hormones” that affect the structure of blood vessels.
Increase the risk of old age
British Medical Journal published an article that traffic noise will increase the risk of elders. Researchers speculate that it may be related to the release of stress hormones and sleep disturbances, leading to coronary heart disease, altering the immune system, and stimulating inflammation.
Causes blood pressure to rise
European Heart Journal published an article that when the noise from road traffic, airplane landing or peer snoring exceeds 35 decibels, a person’s blood pressure will rise, and the louder the noise, the higher the blood pressure.
Make the waist thicker
A four-year follow-up survey in Sweden found that people living in areas with heavy noise pollution have relatively larger waist circumferences. For every increase of 10 decibels in noise, the waist circumference will increase by 1 cm.
Do 5 things to “reducing noise” to life
It is inevitable to deal with all kinds of noise on weekdays. If you want not to be affected by it, you can try to do the following to “reduce noise” in your life.
1. Be careful when renting/buying a house
Ask about the thickness of the floor and wall, and whether it meets the “sound insulation standards”; choose to visit the house at different times, and communicate with neighbors about noise.
When decorating, adding sound-proof ceiling and gypsum board are commonly used methods of sound insulation, and sound-absorbing materials such as sound-absorbing cotton, sound-proof felt and high-density foam board can be added.
The bedroom is the most important resting place, pay attention to 4 principles:
▶Do not choose to be next to the living room, so as not to affect sleep caused by TV and other sounds;
▶Do not choose to be beside elevators, corridors and stairwells;
▶Do not choose a room with a closet, the hollow design will amplify the noise;
▶Do not choose a room that is close to the neighbor’s window, so as to prevent the neighbor’s voice from coming in through the window.
2. Wear noise-canceling headphones or earplugs
If some force majeure causes loud noise, such as decoration sound, you can wear noise-reducing headphones to reduce noise damage; you can wear sleep earplugs to fall asleep, pay attention to frequent cleaning and frequent replacement.
What needs to be reminded is that you should not fall asleep while listening to music with headphones, as this will cause hearing loss and even deafness for a long time.
3. Make positive psychological hints
You can control your perception of noise through psychological cues.
A study found that when participants tried to ignore those noises, their unpleasantness decreased, while their unacceptable ratings for harsh sounds remained the same.
4. Stay away from the noise source briefly
When driving (faster), try not to open the windows, the wind noise may exceed 100 decibels.
When going to bars, sports events and other noisy places, “intermittent” leaving can reduce the damage caused by noise. Even a short break of 10 to 15 minutes will benefit the hair cells of the inner ear.
In addition, you can go to the park to find a quiet place on weekends and enjoy a moment of tranquility.
5. Choose daily necessities with low noise
When choosing household items, such as blenders, soymilk machines, vacuum cleaners, hair dryers, etc., try to choose low-noise ones that are good for your health and reduce the impact on your neighbors.
Do not do to others what you don’t want, everyone should start from self and reduce noise:
If you have indoor exercise habits, it is best to choose resistance exercises. When doing aerobic exercises, you can spread a carpet or shock-proof mat;
The soles of slippers for indoor use should be soft to avoid “snack” when walking; anti-slip mats should be attached to the feet of tables and chairs to avoid noise when pushing and pulling.
If you have children at home, you can lay out foam mats or crawling mats, and tell them not to yell, throw things, or bounce around, and develop a good habit of “silent”.
Comments