
How much can children like excavators?
Babies who can’t sit still even for ten minutes can supervise the work on the construction site motionlessly for most of the day; there are dozens of excavator toys treasured at home, and they can show you their specialties. And not only boys love excavators, but girls also love them.
Playing with excavator toys and watching excavator operations are not enough, and some children’s cartoons also have to be related to excavators.
What is the magic of excavators that make children so obsessed? Let’s find out today~
Children’s psychological needs

Part of the magic of excavators comes from the psychological development needs of children at the corresponding age.
Alisha Wilkins, a child educator and music therapist, said that children have a natural preference for objects that are “loud, big and movable”. These factors can bring children a rich sensory experience.
Excavators account for all three factors. They are loud, big and they can move. They can not only move normally, but also move in a fancy way.
Moreover, in childhood, children’s interest in things appears to be stronger than in other periods.

Generally between 2 to 4 years old, children will show crazy love for certain types of items. Psychologically, there is a proper term to describe this period of children-the period of extremely intense interests, referred to as EIIs. Moreover, boys more commonly present EIIs.
Yale University and the University of Virginia conducted in-depth research on this period of intense interest in children. The researchers collected interviews and questionnaires from the parents of 177 (84 males and 93 females) children. The children were between 11 months and 6 years old (DeLoache, Simcock, & Macari, 2007).
Parents filled out questionnaires and accepted interviews to describe their children’s interest performance to the experimenters. Two researchers will rate the children’s interest level based on the descriptions of the parents.
The results showed that among all interest categories of EIIs, “motor vehicles” topped the list, and the number of children who liked motor vehicles was almost twice that of the second place! The excavator, with its size and variety, can be called the “top class” of the motor vehicle industry.
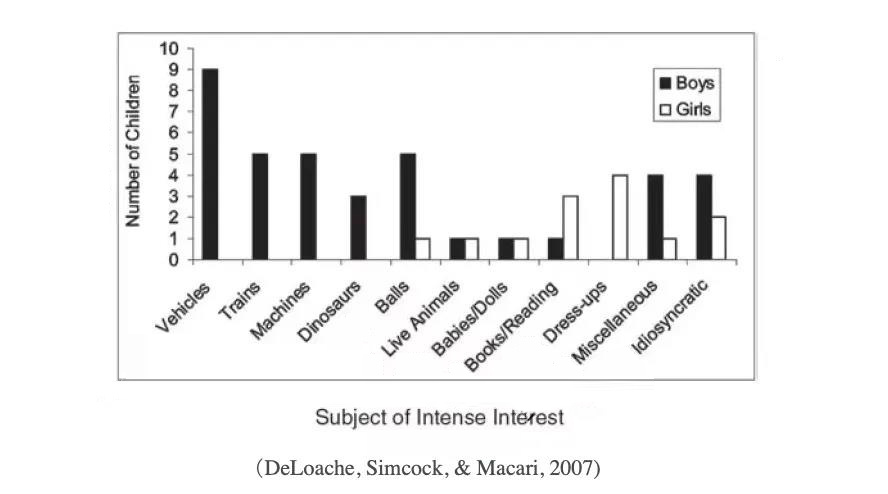
The results of the experiment also show that children will not only like motor vehicles, but also show crazy enthusiasm for items containing the elements of “motor vehicles”.
Look at how the mothers described it in the interview.
When children go to the supermarket, they will look for the trolley pattern on the product packaging.
They love everything as long as it has wheels, no matter that is in book or in the parking lot.
Babies liked wheels from the beginning, and later became interested in cars, fascinated by traffic, fascinated by heavy vehicles, and playing with toy cars for a few hours.
Whether it is abstract like pictures, parts like wheels, groups like traffic, or shrinking like toys, children love them all! This kind of affection can in all aspects.
Therefore, if children like excavators, they may like them in many ways: like excavator toys, watching excavator operations, like photos of excavators, and so on.
The charm of the excavator itself

The magic of the excavator also comes from its own psychological schema of destruction and creation.
According to the famous psychologist Piaget, a schema refers to an organized and repeatable behavior or thinking pattern, and it can also be understood as a network of knowledge and experience in the human brain. For children, it is a “instruction” for their own exploration of the world and interpretation of behavior.
The excavator itself contains a lot of behavior “instructions” that are of interest to children.
On the one hand is the “instructions” of destruction.
The “destruction” here does not mean that children destroy something, but a kind of “destructive play”, which is a game that children like very much before the age of 5.
We can often observe:
Your baby pours a box of toys to the ground at once
Knocks down the tower of building blocks he has piled up
Or grabs a toy and let go on a high place for a free fall
The adults feel distressed when they saw it. and the toys that are bought with money are about to be broken.

In fact, children are exploring the psychological schema behind these behaviors. They are curious about the causal relationship between these behaviors and results. Adults know the results of these actions, but children don’t.
They want to know what will happen after the building blocks are torn down and the toy is released, so as to make a “instruction” of their own destructive behavior.
Excavators can satisfy children’s curiosity and exploration of “destruction”. During excavator operation, there are often “push”, “dump”, “shovel” and other behaviors similar to “destruction game”, which meets the establishment of children’s psychological schema of destruction behavior at this age.
Treasure parents can also try to lead their babies to play some “destruction games”, such as setting LEGO obstacles on the built train track at home, dissecting a small flower outdoors, and trying some special games.
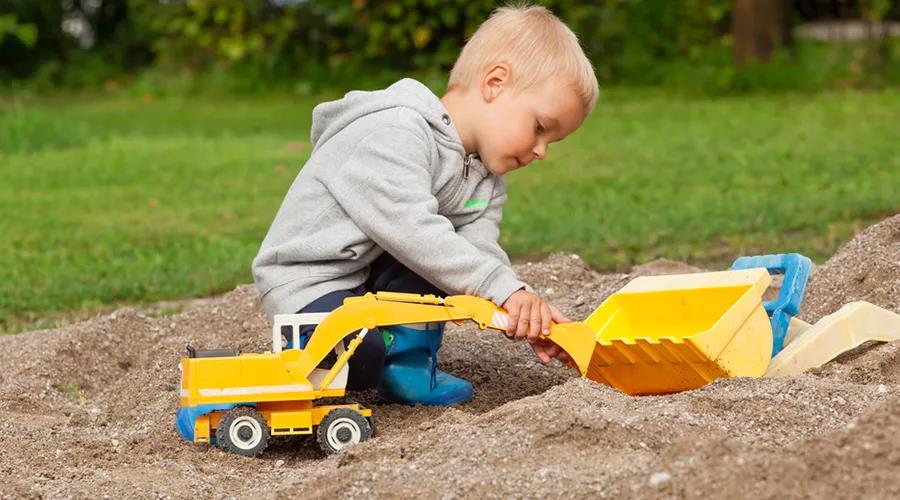

The other is the “specification” of creative behavior.
In English, the word “construction” in children’s game classification represents “constructive play”. Children will use the game materials in the environment to create new things, which can stimulate children’s creativity, such as building high-rise cities with building blocks; Or build a castle with sand.
In many kindergartens in the United States, there is a special “Construction station” construction area play corner, where children will be prepared to play materials such as building blocks, Lego, and excavator toys for children to create freely. It is one of the most popular game corners among children.
At the same time, “Construction” means construction in the city, so when the excavator is working, there will be a warning sign Under Construction next to it-under construction.
There are also many similarities between construction games and excavator operations, and both contain many mental schemas of creative behavior, such as the movement of the excavator when working, the rotation of the fuselage arm, and the children are establishing “trajectories” and “rotations.” Of course, the “build” pattern is also indispensable for the psychological scheme of the excavator. The height of the mound during the construction of the excavator is like a new construction.
These can stimulate the curiosity and interest of children.
The excavator represents the “destructive behavior” on the one hand, and the “creative behavior” on the other side. It is really too hard for children to resist!
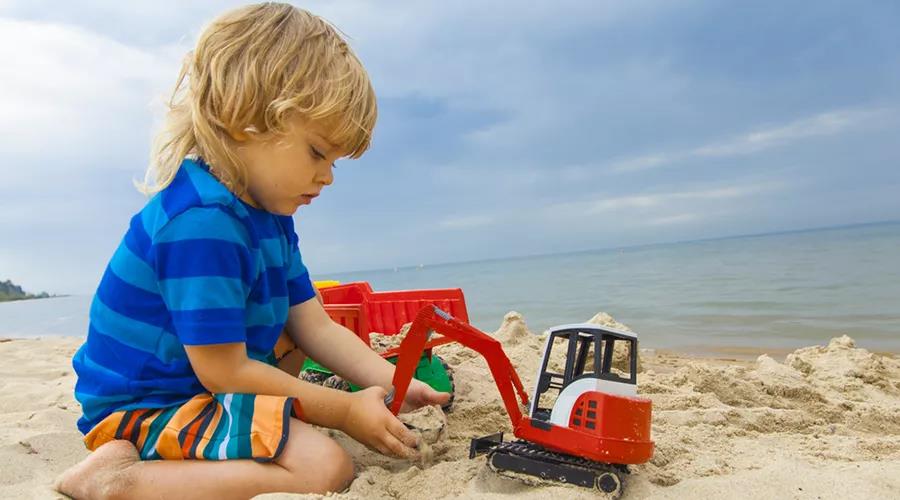

Therefore, children love excavators. On the one hand, it is the psychological needs of children at a certain age. On the other hand, the excavator itself contains the psychological schema of destruction and creative behavior that children and even adults are interested in.
Comments