
All people are created equal, but people have different appearances. Some people say that being good-looking is a natural advantage. Recently, scientists have confirmed this: people with good looks may have a stronger immune system.
In the study published in Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, a research team from Texas Christian University in the United States has shown in the most extensive study to date that individual facial Attraction is related to immune system function.

Good-looking people have stronger immune function?
The study involved 159 participants (79 women) with an average age of 20 years. All participants were tested in advance to ensure no history of chronic medical conditions, no mental illness, no obesity, no use of steroids and anti-inflammatory drugs, no exercise, no alcohol in the 2 days before participating in the study. The researchers assessed each person’s immune system status, body inflammation levels and self-reported health.
The participants’ photos were rated for attractiveness in an online survey by another 492 participants, 259 of whom were women, with an average age of 25.

The researchers found that those rated as “attractive-looking” had relatively healthy immune function, particularly with regard to bacterial immunity.
There was no link between higher levels of inflammation and attractiveness among the participants. This may suggest that facial attractiveness is a better proxy for a strong immune system than signs of acute illness.
In short, the main role of facial attractiveness may not be to avoid a sick partner, but to avoid a partner that may affect the health of your future offspring.
The researchers say this is not enough to determine why human aesthetics exist and that facial attractiveness may serve some evolutionary purpose. Further research is needed to verify and explore what drives the link between physical attractiveness and immune function.
Immunity is the body’s bodyguard
As the escort force of human health, the immune system is mainly composed of two parts: innate immunity and acquired immunity. When people are sick, whether it is innate immunity or acquired immunity, they will fight the enemy bravely.
innate immunity
At birth, the first echelon is the skin, mucous membranes, and mucous membrane secretions, such as lactic acid, fatty acids, gastric acid and enzymes. The second echelon is bactericidal substances and phagocytic cells in body fluids, such as neutrophils, macrophages, etc., which have a defensive effect on a variety of pathogens.
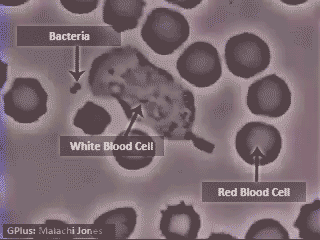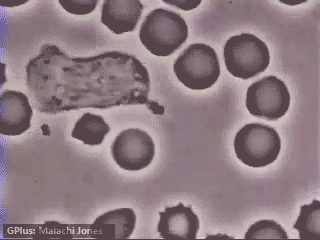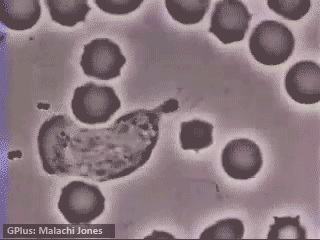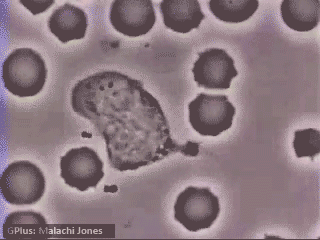
Neutrophils “chasing” Staphylococcus aureus
acquired immunity
After a person is born, it is gradually established through constant exposure to new things, and it only acts on a specific pathogen or foreign body. The surrounding environment has a great influence on it, and the acquired immunity of different people is also very different.
The acquired immune system is composed of immune organs (including thymus, lymph nodes, and spleen), immune cells (such as T lymphocytes, B lymphocytes, etc.), and immune factors.
When the body plays an immune role, it also produces some immune molecules, including immunoglobulins, complements, and various cytokines, chemokines, etc.
The stronger the immune system, the better
The immune system needs to be in a state of balance for the body to be healthy. When the immune system is out of balance, two phenomena generally occur:
weakened immunity
At this time, the body is prone to various diseases caused by viruses or bacteria, such as viral colds.
Tumors are formed by a similar mechanism: The tumor cell is so smart that it produces substances that make the “guards” watching it fall asleep and grow unscrupulously unattended.
A paper published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences speculates that a weakened immune system is the primary cause of the increased incidence of cancer.
strong immunity
The immune function is too strong, and immune cells will attack non-disease factors (such as pollen, hair, etc.) from the outside world, resulting in allergic reactions.
In severe cases, immune cells may even attack their own normal tissues and organs, causing autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Women are more likely to develop certain autoimmune diseases.
It should be reminded that people of different ages face different “immunity crisis”:
Children and adolescents: In the past, the environment was unsanitary and prone to infectious diseases caused by parasites, bacteria or viruses; now the environment is too clean and may be plagued by allergic diseases.
Middle-aged people: After the age of 30, the immune function of the human body begins to decline. The middle-aged period is the stage of the greatest economic pressure and mental pressure. The irregular work and rest, and the lack of nutrition can cause problems in the immune system.
Seniors: After age 65, immune function inevitably takes another step forward. It is easy to catch colds, allergies, infections, frequent insomnia, loss of appetite, fatigue, sallow skin and thin muscles, etc., pay attention to immune disorders of the body.
7 things to fill in the “immune short board”
There are many factors that affect the immune balance. Genetics, age, emotions, stress, sleep, diet, environment, etc. can make the immune imbalance. If you want your immune function to function normally, you can do the following small things in your life.
cold and warm
In winter and spring, the temperature fluctuates greatly, and some people’s immune systems are unstable, which is easy to cause diseases, especially the elderly and children, pay attention to keeping warm and cold.
Within the normal body temperature range, the higher the body temperature, the stronger the immunity. Because high body temperature is beneficial to activate more immune cells in the human body, which can better destroy invading pathogenic microorganisms.
Manage chronic diseases
People with underlying diseases have poor immunity, so they should follow the doctor’s advice for treatment, control the disease well, and do not give the virus an opportunity.
Nutritional balance
Under the premise of ensuring a variety of foods and a balanced diet, adequate supplementation of the following 7 nutrients can help enhance the body’s defense against diseases.
moderate exercise
Exercise can help improve cardiopulmonary function and enhance the body’s tolerance under virus infection. Scientific research shows that long-term moderate exercise can protect the body’s immunity and reduce the risk of infectious diseases.
Work and rest rules
Staying up late can disrupt the body’s biological clock and affect the immune system’s ability to respond and defend. It is recommended to maintain a regular schedule and sleep 7-8 hours a day to help maintain the natural rhythm of the immune system.
stable mood
A Stanford University study found that laughter can increase the number of antibodies and immune cells in blood and saliva.
It is recommended to maintain a happy mood, especially for the elderly, do not be overly anxious and panic, and reduce psychological pressure by exercising, reading, chatting with relatives and friends, etc.
Vaccination
Vaccination is an important means of enhancing immunity to certain diseases, and it is also the most cost-effective way to prevent infectious diseases, especially for children and the elderly.
Comments