
Have you ever seen some old people like that, when they talk, they lose their minds and their words do not express their meaning; they still look around when they are holding things in their hands; some can’t even find their way home…
Alzheimer’s disease (commonly known as “senile dementia”) is a common disease in the elderly. There is no cure for it, but early prevention can protect cognitive function and delay the occurrence of the disease.
Recently, a Danish multi-year follow-up study in the European Heart Journal (the longest sample is lasting for 25 years) proposed a dementia risk prediction map, which predicts the risk of dementia within 10 years based on the status of risk factors.
Dementia risk prediction map
This study involving more than 60,000 people found that the strongest predictors of dementia were old age, low education, diabetes, high blood pressure, smoking and genetic factors.
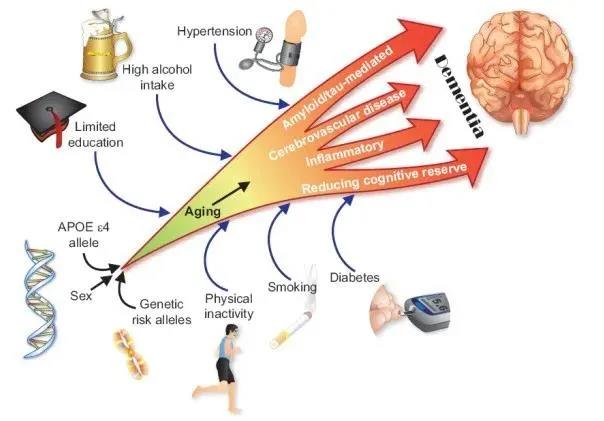
(Risk factors for dementia)
For the first time, researchers have proposed a dementia risk prediction map, which predicts the risk of dementia within 10 years based on the status of risk factors.
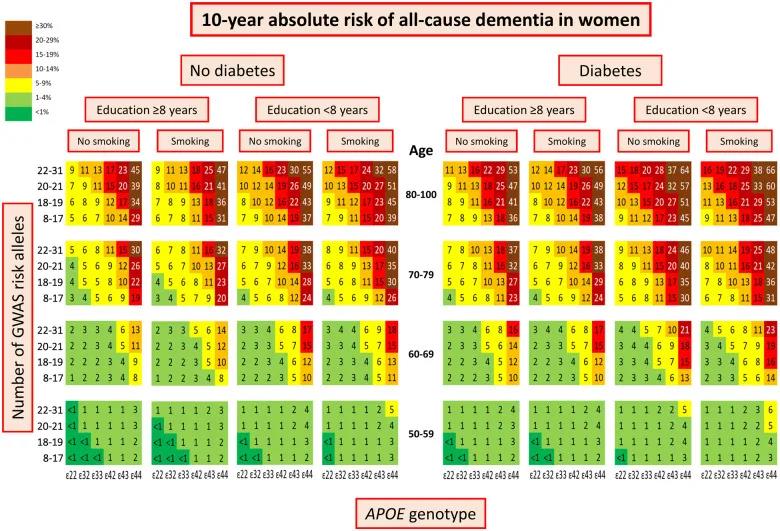
(Risk of dementia in women)
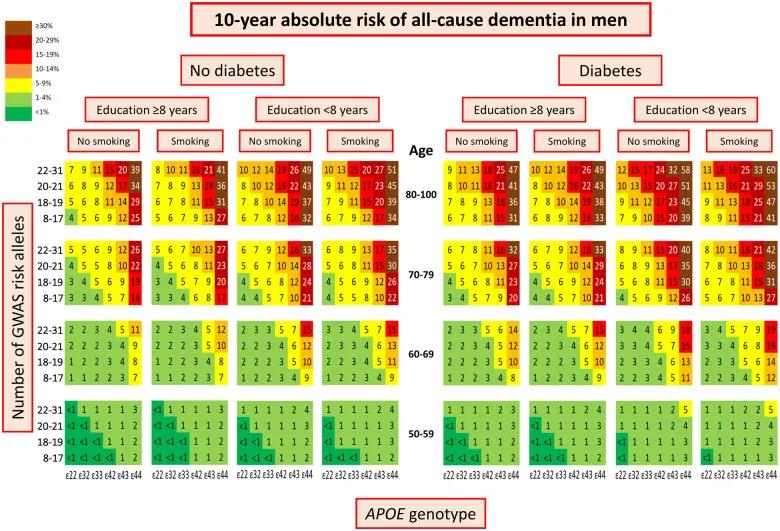
(Risk of dementia in men)
Studies have shown that, overall, the risk of dementia increases with age. The more risk factors for dementia, the greater the probability of disease, and this rule is more obvious in women.
If a woman has low education, who is smoking and has diabetes, her apolipoprotein E genotype is 4 (risk factor), and there are 30 risk genes that are highly associated with dementia, then when she is 50-59 years old, 60-69 years old , 70~79 years old and 80~100 years old, the risk of developing dementia is 6%, 23%, 48%, and 66%, respectively.
Men with the same risk factors have a relatively low risk of developing dementia at the same age, at 5%, 19%, 42%, and 60%, respectively.
The uniqueness of this study is that it not only confirms the previous belief that lifestyle and cardiovascular risk factors are related to dementia, but also conducts genetic testing for subjects, including 20 to 30 genes with higher dementia risk into the assessment scope.
This also shows that genetics is still an important risk factor for dementia. But the study also pointed out that even people with a high age and a family genetic history can still reduce the risk of dementia through active lifestyle interventions.
When dementia first occurs, it can be found through signs in life. See a doctor as soon as possible to get a better treatment effect.
Memory loss. Many commonly used things cannot be found. Things are always lost. Many things cannot be remembered and need to be written in a notebook.
Daily housework becomes difficult. For example, One used to be very good at cooking. After getting this disease, he became reluctant to do it, or could only do very simple meals.
Change of temper. Some people used to be enthusiastic and cheerful, and gradually became suspicious of family stealing or their spouse having an affair, causing family discord.
The behavior becomes strange. Putting dishes in the washing machine and using shoe covers as hats are signs that the old man’s judgment is not normal. It is a very obvious sign that the elderly cannot find a home. Even if it happens occasionally, they should seek medical treatment in time.
Forgetfulness is not necessarily Alzheimer’s
As you get older, your memory will decline, and some elderly people worry that they may suffer from Alzheimer’s disease. In fact, memory impairment is indeed the earliest sign of Alzheimer’s, but there are many reasons for memory impairment, such as normal aging, mood disorders, and hypothyroidism. Among them, the most easily confused with Alzheimer’s is normal aging.
Forgetfulness is one of the common manifestations of aging. As we age, all parts of the body, including the brain, will change. Many people feel that it takes longer to learn new things, their memory is not as good as before, they often can’t call their old friends, they can’t find glasses, or they forget their keys.
However, these symptoms are usually mild forgetfulness, rather than serious memory problems, which are fundamentally different from Alzheimer’s.
If memory loss only occurs, don’t worry blindly. The brain’s functions include language, memory, visual space, emotion, personality, and cognition. At least 2 to 3 items are damaged before it can be regarded as Alzheimer’s.
Generally speaking, the difference between the two is reflected in the following 6 aspects:
01. Near memory disorder & instant memory disorder
Senile amnesia is manifested as near memory impairment, and it is partial, which can be remembered after being prompted, while Alzheimer’s disease is mainly composed of transient memory impairment, which is complete and cannot be remembered after being prompted.
02. No cognitive impairment & impaired time, place, and numeracy
Senile amnesia is not accompanied by cognitive impairment, while patients with Alzheimer’s disease are often accompanied by obstacles in time, place, and numeracy.
03. Maintain normal conditions & indifference
Forgetful old people will maintain normal emotions such as happiness, anger, sorrow, and joy, while patients with Alzheimer’s disease often become indifferent and lack of basic emotional performance.
04. Clear thinking & confusion
The forgetful elderly have clear thinking, language skills and reasoning and analysis skills, while Alzheimer’s patients have confused thinking, poor language, and lack sound reasoning and analysis skills.
05. Very anxious about poor memory & not aware of memory decline
Forgetful elderly people often appear to be very anxious about poor memory, while patients with Alzheimer’s disease are not aware of the decline in their memory.
06. Have the ability to take care of life & gradually lose the ability to take care of life
Forgetful elderly people can maintain normal self-care ability, while elderly people with Alzheimer’s disease will gradually lose the ability to take care of themselves even if they have no physical disease.
Prevent old idiots, beware of the three major causes
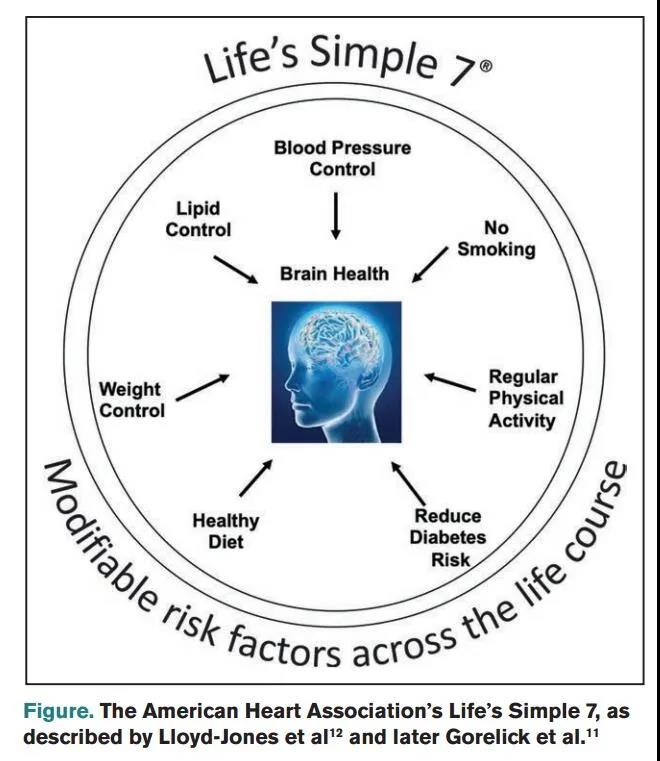
On March 15, the American Heart Association (AHA) issued a scientific statement on the primary prevention and treatment of brain health in response to the impact of the “silver tsunami”.
The statement emphasized that Life’s Simple 7, blood pressure, blood lipids, blood sugar, smoking, body mass index, healthy diet and physical activity should escort the health of the brain throughout life.
Alzheimer’s is an age-related disease, and patients over 65 years old account for the vast majority. With age growing, the incidence rate rises sharply.
The incidence rate is about 1/3 for people over 80 years old and about 1/2 for people over 90 years old. Although the exact cause of the Alzheimer’s is not yet clear, Tang Yi analyzed that the three risk factors of less exercise, high blood pressure and low education are likely to have an impact through the following mechanisms:
Less exercise
Generally , elderly people who exercise less often have poor control of blood pressure, blood sugar and blood lipids. Cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases tend to come to the door and cause vascular damage.
On the other hand, many studies have shown that exercise can increase the secretion of nerve growth factor and promote blood circulation, both of which are conducive to maintaining brain function. On the contrary, too little exercise can not benefit the brain.
High blood pressure
Hypertension is a risk factor for cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. It can cause chronic cerebral ischemia and hypoxia and damage to the vascular structure. It can also cause damage to the brain tissue and increase the risk of senility.
Low education
The number and structure of brain neurons in newborn babies are similar, but due to different levels of later education, the degree of brain training and development is also different, and the number of neuronal synaptic connections formed in the brain is different, which affects cognition in later years.
Reminder: Family members should go to memory clinic of the hospital for screening as soon as possible when they find that their memory is significantly decreased or abnormal.
If parents, siblings and other immediate family members have a history of Alzheimer’s disease, their risk of suffering from Alzheimer’s disease is 2 to 4 times higher than that of ordinary people, and it should be prevented as soon as possible.

At present, there is no cure for Alzheimer’s disease in the world, but early prevention can protect cognitive function and delay the occurrence of disease.
It is recommended that the elderly adopt 4 methods that have been confirmed by research and can effectively delay cognitive decline in joint intervention:
Strengthen cognitive training. Don’t stay still or watch TV for a long time. You must consciously engage in mental activities such as playing chess and reading. You can also play some puzzle games on the computer;
Ensure a certain amount of physical exercise, 3 to 4 times a week, aerobic exercise for a total of more than 180 minutes, plus a moderate amount of strength training;
Adjust your diet, eat more vegetables, fruits, deep-sea fish, beans, and eat some olive oil in moderation;
Actively control the risk factors of Alzheimer’s, such as high blood pressure, obesity, diabetes, etc.
Comments