
For many people, one of the happiest things in winter is to take a hot bath and rub the mud, then apply a thick body lotion, lie in the bed, and feel the whole person relaxed.
Among them, the step of taking a bath will bring unimaginable happiness. Some people say that the harder you rub, the pleasure you feel after rubbing your smooth skin.

Bathe hard, causing two kinds of damage to the body
When taking a bath, many people like to use a bath towel to rub vigorously, until the body appears “mud”, they will feel clean, but in the eyes of a dermatologist, scrubbing too hard may increase the risk of skin diseases.
The “mud” produced by the bath is the exfoliated cells produced by the body’s daily metabolism and the oil secreted by the body. The body’s sebaceous glands secrete about 150 to 250 grams of oil every week. They form a film on the surface of the skin, which not only protects the body from external damage, but also prevents the loss of nutrients, especially moisture, in the body.
Destroy the stratum corneum
The stratum corneum and lipid film on the skin surface together constitute the barrier protective layer of the skin, and rubbing with a bath towel will indeed destroy this protective film.
When the stratum corneum is scraped off in a large amount, the skin barrier structure will be weakened, creating favorable conditions for the bacteria and microorganisms colonized on the skin surface to invade. Once abraded, there is a risk of infection.

Dermatologists said: In addition to rubbing the dead skin, the hard bath also rubbed off the skin emulsified film, destroying the barrier, and causing itching.
Inducing or aggravating skin diseases
Rubbing hard until it is red, it is easy to cause skin cracking or itching. If you use soap and shower gel, the skin will become drier and cause dry dermatitis.
How to judge that I have “rubbed” excessively?
If you can hear a squeaking sound when rubbing your skin with your fingers after washing, it means you have over-washed. It is recommended to take a bath frequently, but not to “catch up and wash, rub hard.”
The 6 most common mistakes in bathing
Although taking a bath may seem simple, washing it incorrectly can also harm your health. In addition to scrubbing vigorously, these habits should also be changed together.
Bathing too often
Excessive bathing will eliminate the beneficial bacteria on the skin surface, reduce the body’s ability to resist foreign bacteria and viruses, and increase the risk of infection. Moreover, too much bathing will take away the oil used for moisturizing on the skin, disrupt the water-oil balance, and cause dry skin.

In summer, the human body secretes vigorously and sweats more, so it should be washed once a day. The weather is not hot in winter, spring, and autumn, so there is no need to take a bath every day.
The specific bathing frequency should vary from place to place: when it is hot in the south, it is not an exaggeration to wash twice a day. When it is cold in the north, twice a week is not too small.
People with fatter body and strong sebaceous gland secretion can increase the number of baths appropriately. The secretion of sebaceous glands in the elderly is reduced, and the number of bathing can be appropriately reduced.
Taking a bath too long
Control within 20 minutes. Bathing time is too long, it is easy to make people fatigue, easy to cause cardiac ischemia, hypoxia.
Bath water is too hot
Taking a bath with hot water can relieve fatigue, but it will cause dry skin and itching.
Some elderly people use hot water to scald the itchy parts, which can worsen the symptoms. Hot water scalding can aggravate the damage to the skin barrier, scalding and itching stimulate the same nerve endings, and the skin becomes more itchy.
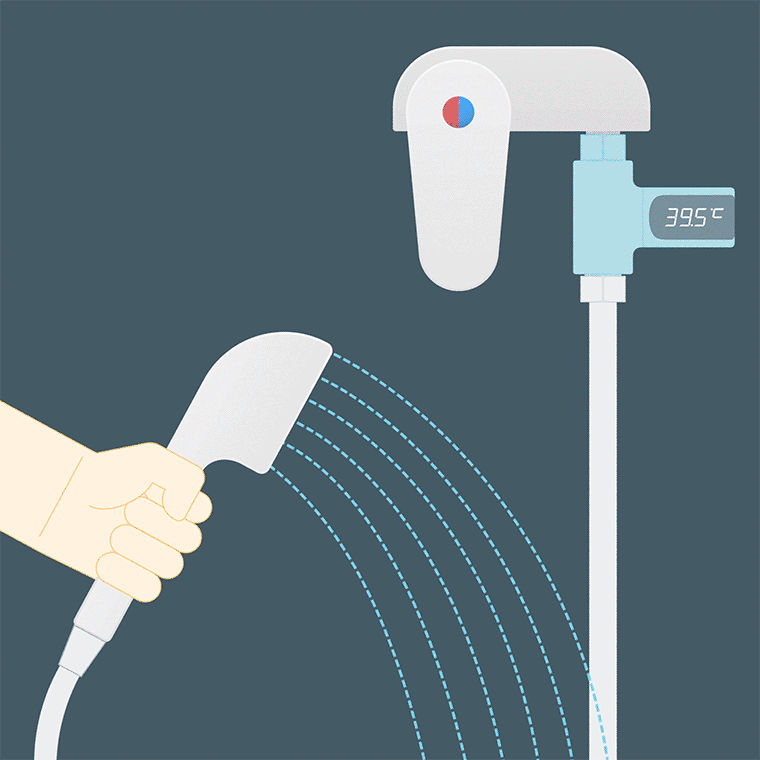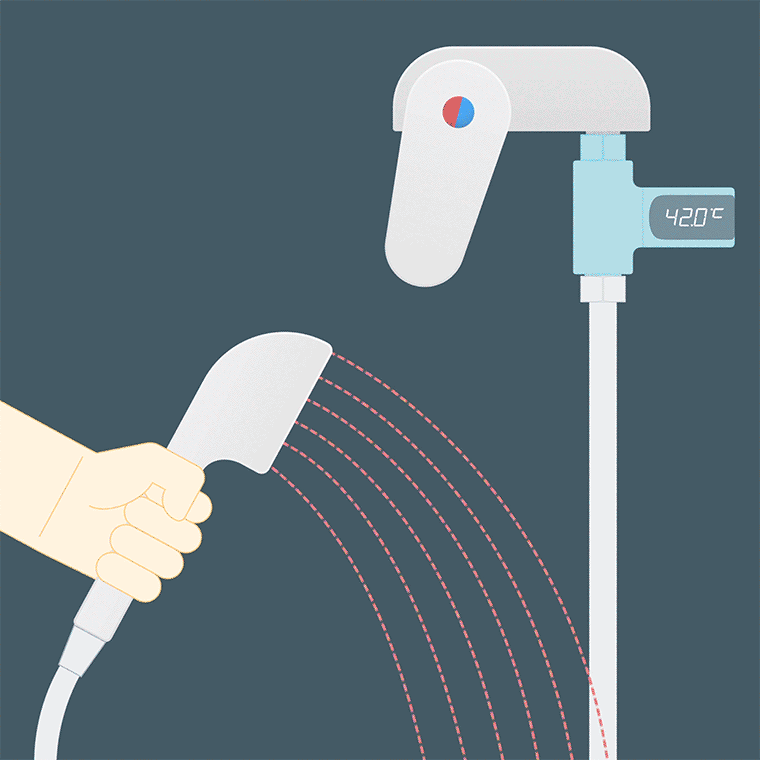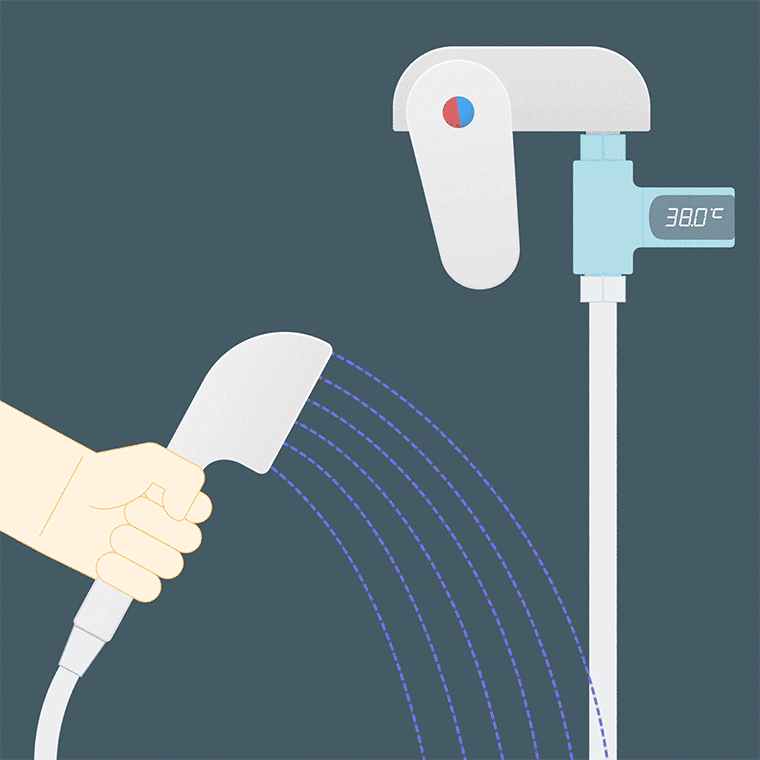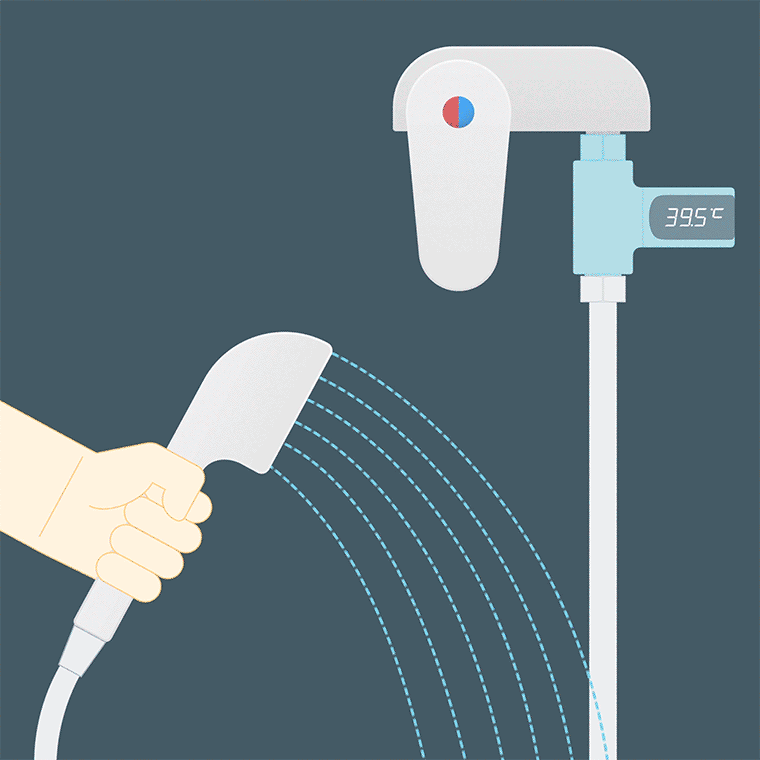
The temperature of the bath water should be 38°C~40°C, and it is not recommended to be higher; the temperature of the bath water for patients with cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases should also be lower, and it is advisable to keep it at about 35°C.
Use soap
The pH of the skin is related to itching. The higher the pH (alkaline), the easier it is.
If the skin already has itching, avoid using alkaline soap when cleaning, and it is not recommended to use it frequently.
Flush face with water directly
The skin of the face is relatively delicate, and the water directly on the face will cause great irritation to the facial skin, rupture the capillaries of the face, make the face red, and more likely to cause facial allergies.
Do not clean the bath ball
The bath ball is porous and wrinkled, easy to hold dirt. In addition to microorganisms in the air, human dead skin, dirt, and bacteria will also accumulate. It is best to clean it thoroughly every 1 to 2 weeks and replace it every 2 to 3 months.
How to prevent dryness in bathing in winter?
After entering the winter, sweat secretion is significantly reduced, and the skin becomes abnormally dry. The level of androgen in middle-aged and elderly people decreases, and the sebum decreases, and the skin loses the most powerful “weapon” against dryness. Although young people are rich in sebum, if they wash frequently and use detergents with strong degreasing effect, the skin will be dry, can also cause pruritus. In winter, you should pay attention to the following points:

01. Use less or no shower gel
Bath lotion is a chemical synthetic detergent, long-term excessive use, the chemical substances in it are too much absorbed by the body, it will cause dryness, allergic dermatitis, etc. You should try to choose a shower gel with no fragrance and simple function. A one-yuan coin is enough for each use.
02. Always bathe in clean water
The elderly and young children with weaker skin should use clean water as much as possible. Cleaning products such as body wash should be used once a week. For ordinary people, the limbs that produce less oil and are easy to dry can also be washed with water only. Note that the water temperature is not easy to overheat, otherwise it will aggravate itching and dryness.
03. Apply moisturizing cream after bathing
After taking a shower, apply moisturizing cream on your arms and legs to relieve symptoms such as dryness and itching. Vaseline, urea, silicone oil, etc. are all good choices. According to the dryness of the skin, choose the right product and application times until the skin is moisturized. If you usually suffer from eczema and have sensitive skin, you can choose moisturizers that do not contain fragrances and preservatives to reduce the risk of allergies.

Some elderly people like to scald with hot water and use strong alkali soap to wash. Coupled with air conditioning and heating, the loss of water is even worse. These improper stimulation and warm indoor environment are the main accomplices of winter pruritus. It is recommended to use a humidifier in air-conditioned or heated rooms to increase air humidity.
Comments