
Human eyes are like two high-definition cameras, which are continuously running and capturing images every minute and every second while your eyes are open.
But you may not know that both eyes do not always work at the same time. One of the eyes is responsible for the main visual task, while the other is quietly “lazy”…

How to judge your “common eye”? What behavior will hurt it?
One eye is quietly “fishing”
Just as our hands are divided into “left and right-handed”, our eyes are also divided into “dominant eyes” and “secondary eyes”. Even if the eyes are looking at the object, the effects of the two eyes are not even.
The image obtained by one of your eyes is faster and has a higher priority in the positioning process, while the other eye is always “fishing” and is in the auxiliary state to cooperate with the movement. The dominant eye is the dominant eye.

The dominant eye is also called the dominant eye. Its resolution is higher, and what you see will be accepted by the brain first; the secondary eye is mainly used to observe the background and has high color sensitivity.
The brain habitually uses the imaging of the main eye to analyze and locate objects. Due to more movement, it gets more supplies. The main eye often develops better than the secondary eye.
If the main eye is regarded as a high-definition main camera, the auxiliary eye is wide-angle and depth-of-field; their formation may be related to genes or behavior habits in childhood.
Is your dominant eye the left eye or the right eye?
Which eye is working hard and which eye is quietly “catching fish”?
In addition to going to the hospital or a regular optician for optometry, you can also try a simple preliminary identification.
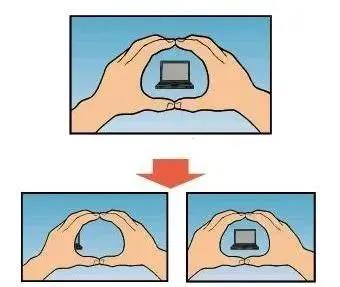
Open and close your hands together, forming a triangular or circular gap with your tiger’s mouth.
Looking for the target object, it can be a pen or a computer; the body is facing the target, and the eyes are looking at the object squarely.
Place the target object in the middle of the gap between your hands, then close the left and right eyes alternately, and observe the displacement of each eye to the target object:
If the displacement of the target object is small, the eye that is open at this time is the dominant eye; if the displacement is large, the eye that is open is the secondary eye.
Confirm the meaning of the dominant eye
Some people may experience dizziness and eye pain after wearing glasses, which may be caused by the secondary eye occupying the dominant position.
Therefore, when performing professional optometry and correcting and adjusting vision, try to ensure that the adjustment of the main eye is sufficiently accurate.
The principle of refractive surgery is the same as that of optics to correct vision. The above-mentioned optics principle should also be followed in the design of surgery, so that the visual acuity level of the dominant eye after surgery is not lower than that of the non-dominant eye.
In addition, in some sports that have high requirements for aiming accuracy (archery, shooting, etc.), it is also important to determine the main eye and use the main eye to aim.
These habits are quietly hurting the eyes
The main visual eye has a heavy workload. If it is not properly protected, some bad habits will make the eyes more and more tired, and the power will increase again and again.
Always staring at the screen
Faced with various screens such as computers and mobile phones for a long time, the frequency of blinking will naturally decrease, reducing to 4-6 times per minute.
When people look at the screen, keeping a certain focal length for a long time will induce visual fatigue. The common symptoms are the inability to work at close distances, pain around the eyes and orbits, blurred vision, dry eyes, and tears.
Like “high brightness”
Under strong light stimulation, the pupils will shrink protectively, causing spasm of the pupil dilator muscles, eye pain, dizziness and headache. Pupil shrinkage can also cause the lens to become convex, and the focus will be strengthened, leading to a rapid increase in myopia.

If you don’t turn on the background light when watching TV, or when you watch your mobile phone in the dark, the contrast between bright and dark is too strong, which can also cause problems such as pupil sphincter spasm and visual fatigue, and promote the formation of myopia.
Wrong vision posture
Many people’s “fixed posture” every night: lying on their side and looking at the mobile phone, it may cause differences in vision between the eyes and even anisometropia.
Always close vision and incorrect posture will make the adjustment ability of the eyes worse and worse.
Protect your eyes anytime, anywhere
The maintenance of eyesight should not only focus on the dominant eye, but the protection of both eyes is equally important.

Adjust screen brightness
It is recommended that the brightness of mobile phones, computers, and TVs is set to 60%, not more than 80%.
In addition, all screens need suitable background light. When using projector equipment at home, the brightness and contrast should be adjusted to a balanced state, and the background light should be appropriately dimmed as needed, but it cannot be viewed in complete darkness.
Turn on eye protection mode
In general smart phones in the “eye protection mode”, the blue light will be reduced by about 30% to 40%, which has a certain effect on reducing visual fatigue.
The eye protection mode that comes with electronic products is more comprehensive and effective in anti-blue light. It usually protects the eyes by shielding blue light (such as adjusting the color temperature) and adjusting the brightness of the screen.
Change eye habits
Increase the frequency of daily blinking, especially when looking at the screen; do not rub your eyes with your hands on weekdays, apply heat to your eyes before going to bed.
Extend outdoor activity time
Outdoor activities are of great significance to prevent myopia and relieve visual fatigue. Proper exercise, even just going for a walk, can relax your eyes.
Supplement yellow-green food
Carrots, corn, tomatoes, broccoli and other yellow-green foods are rich in lutein, which is converted into zeaxanthin in the human body to help protect eyesight.
Comments