Gallstones refer to the formation of “super concentrated” bile in the gallbladder or bile ducts.
A gallstone is as small as a grain of sand, and as large as a golf ball. In the event of an attack, the tough guy will be stunned in the first second; the next second he will hold his stomach and roll all over the floor.
Epidemiological surveys show that the incidence of gallstones in the Chinese population is 8% to 10%. Among them, most patients with gallstones have a common habit-skip breakfast.
How do gallstones come from?
Why not eat breakfast and get gallstones?
Among female patients with gallstones between the ages of 20 and 35, 80% to 90% of patients with gallstones have the habit of skipping breakfast.
Why not eating breakfast will increase the risk of gallstones?
The bile in the gallbladder can only be discharged from the gallbladder under the stimulation of food. After three meals a day, the gallbladder discharges bile regularly.

When I got up in the morning, the gallbladder that had rested all night was full of stored bile. Eating breakfast at this time can stimulate the gallbladder, which will excrete bile into the intestines in time to help digestion.
Without breakfast for a long time and without food stimulation, the bile in the gallbladder has no chance to be discharged. The increase in bile concentration causes the precipitation and deposition of cholesterol, which will form gallstones over time.
The summary is: skipping breakfast does not necessarily cause gallstones, but most people suffering from gallstones do not eat breakfast.
Why do gallstones favor women over men?
Another notable feature of gallstones is that “women are preferred over men”, and the incidence rate of middle-aged women is as high as 15%. Statistics show that the incidence of gallstones in women is 2 to 4 times that of men.
Why are gallstones easier to target women?
This is because sex hormones in women affect the chemical composition of bile and the contractile function of the gallbladder, which in turn promotes the formation of stones.

After getting gallstones, some patients will not have any symptoms, while some will have biliary colic, namely: severe pain in the upper middle or upper right abdomen, restlessness, sweating, pale complexion, nausea and vomiting, and even Jaundice and high fever appear.
Because the pain site of gallstones is similar to the site of stomach pain, it is easy to confuse. The pain caused by gallstones is often mistaken for stomach pain.
In fact, there is a difference between stomach pain and gallstone pain:
Pain area:
When stomach pain occurs, it is usually in the mid-abdomen. When a gallbladder stone occurs, it is usually pain in the right upper abdomen, and it is often accompanied by radiating pain in the right shoulder.
Timing of pain:
When stomach pain occurs, it is usually pain when you are hungry; when a gallbladder stone occurs, it is generally painful after a meal, especially after eating greasy food.
As a common disease, gallstones are often ignored by people. If they are not treated in time, they may cause gallbladder cancer. According to statistics, 80% of gallbladder cancers are related to gallstones, and the incidence is positively correlated with the size of the stones and the length of the disease.
When these symptoms appear, you should seek medical attention in time, and the initial diagnosis can be confirmed by abdominal ultrasound examination. Ultrasonography is painless and convenient, and is the first choice for diagnosis.
Seven kinds of people are easy to get gallstones
According to the causes of gallstones, there are seven kinds of people who are more susceptible to diseases in life, and they need special attention.
People who sit still after a meal
If you don’t like exercise and physical activity is reduced, the contractility of the gallbladder muscle will decrease. Delayed bile emptying can easily cause cholestasis, creating conditions for the formation of gallstones.
In particular, some people like to sit on the sofa and watch TV or play on the computer after a meal, and eat a variety of snacks while watching. This is one of the important reasons for gallstones.
Obese people
Obesity is an important factor in the formation of gallstones. The incidence of gallstones in obese women aged 20-30 years is 6 times higher than that of their normal-weight peers. 40% of obese women over 60 have gallbladder disease and gallstones.
Those who don’t like breakfast
If you do not eat breakfast, and the fasting time is too long, bile will accumulate in the gallbladder for a long time and become 100% concentrated bile, which will easily lead to the formation of stones.
Those with a preference for meat and sweets
Such people usually consume a lot of fat and cholesterol and tend to form cholesterol stones. Too much sweets will promote insulin secretion and accelerate the deposition of cholesterol.
Women with multiple pregnancies
Women account for 70% of gallstone patients, and the more pregnancies, the higher the incidence.
The reason is that the high level of estrogen in the female body will affect the formation of bilirubin glucuronide in the liver and increase the unbound bilirubin; estrogen affects the emptying of the gallbladder, causing bile stagnation, and it is easy to form stones.
Long-term oral contraceptives
Such people are twice as likely to suffer from gallstones than others. Women who are treated with estrogen drugs after menopause also suffer from gallstones. This may be related to the effects of sex hormones.
People with family history of disease
People with this genetic gene are more likely to suffer from gallstones than the average person.
Patients with gallstones need to pay attention to the following points in their diet:
1. Be sure to eat breakfast; 2. Strictly control fat and cholesterol intake; 3. Reduce refined white rice noodles; 4. Drink plenty of water, drink no less than 2000 ml of water a day, which can dilute bile and promote its excretion; 5. Reduce oxalic acid Ingestion, spinach, amaranth, lettuce and other vegetables rich in oxalic acid, blanch them in boiling water before cooking; 6. Eat less sour food.
Four types of gallstones must be cut off
When gallbladder stones are found on physical examination, most of them are asymptomatic. About one-third of patients will have abdominal pain or other symptoms within 5 years, but most of them will have no obvious symptoms for life.
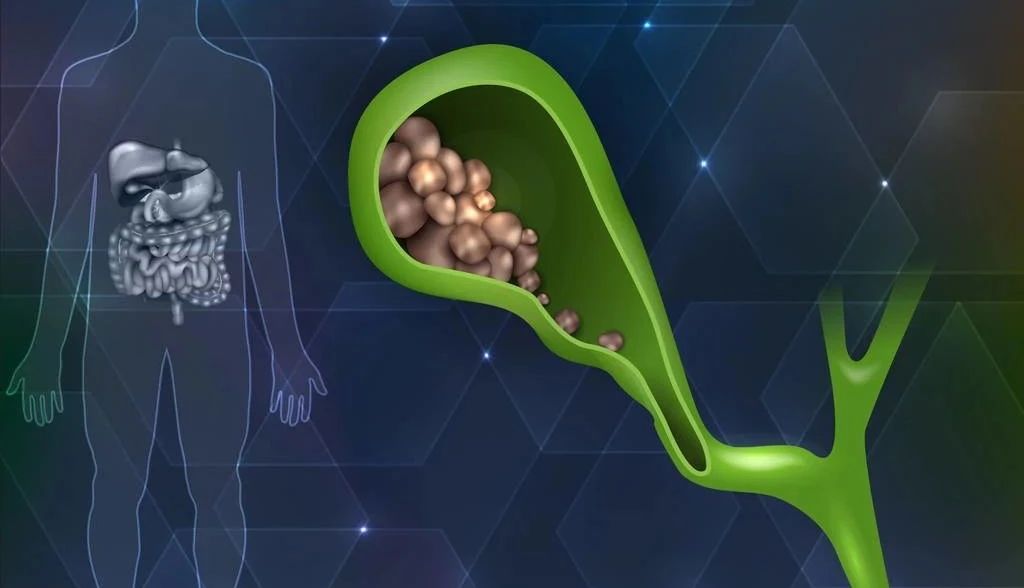
Among asymptomatic patients, only a very small number of stones shrink after diet control, lifestyle changes, and medication, and most of them remain as they are. Therefore, general doctors will recommend regular physical examinations and observations. What kind of gallstones are dangerous and must be cut off?
Silt-like stones
These stones are generally a few millimeters in diameter and are easily discharged by the gallbladder into the common bile duct, causing secondary bile duct stones, biliary obstruction, cholangitis, biliary pancreatitis, and in severe cases can lead to acute obstructive suppurative cholangitis or acute severe pancreas Inflammation, endangering the life of the patient.
Stones with a diameter of about 1 cm
They are easy to jam the outlet of the gallbladder. Because it jams the neck tube of the gallbladder (gallbladder outlet), it causes long-term inflammation and adhesion. The stones will eventually jam the outlet, causing purulent cholecystitis, and even gallbladder necrosis and perforation.
Stones larger than 3 cm in diameter
They are considered to have a high possibility of causing “malignant change”.
“Magnetized Gallbladder” Stones
Gallbladder full of stones, gallbladder atrophy, etc., there is a certain risk of cancer.
Gallstones are different from kidney stones. Shaking and removing stones cannot be used. Surgical treatment is generally recommended.
For gallstone patients with important organ diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, emphysema, renal insufficiency, cirrhosis, etc., corresponding adjuvant treatment must be given to improve the safety of surgery.
Comments