Although I have to thank the invention of air conditioner every summer to save my life
Just a few days ago, the night when the air conditioner suddenly broke down, my feeling was particularly profound
The room was as hot as a sauna room, and there was no wind when I opened the window
Recalling the days when there was air conditioning, I felt that I really didn’t know to cherish it.
In the sleepless night, I was curious that in the ancient residence without air conditioning, how did they avoid the heat in summer?
Taking the Middle East and India as examples, many ancient summer vacation measures are listed
After reading that, I felt the ancient people were really smart.
If I lived in their house, I don’t have to worry about the air conditioner breaking anymore
To be isolated from hot air
Most buildings in the Middle East and South Asia have thick walls (even up to a few meters thick), but the windows are small and few in number.
Thick walls can effectively insulate heat, and small windows prevent sunlight from entering.

For example, in the inner courtyard of Red Fort in Delhi above, except for the reception hall in the middle and the color Palace on the right (part of the harem), most buildings are painted with thick walls and small windows.
Evaporative refrigeration

There is an ingenious design in the Rang Mahal. A canal passes through the palace and enters the central pool. In hot summer, water evaporates and absorbs heat, which can play a certain role in cooling.
The Rang Mahal also has a basement. When the weather is too hot, you can go to the basement (due to the thermal insulation of the soil, the basement in summer is generally much cooler than the ground).
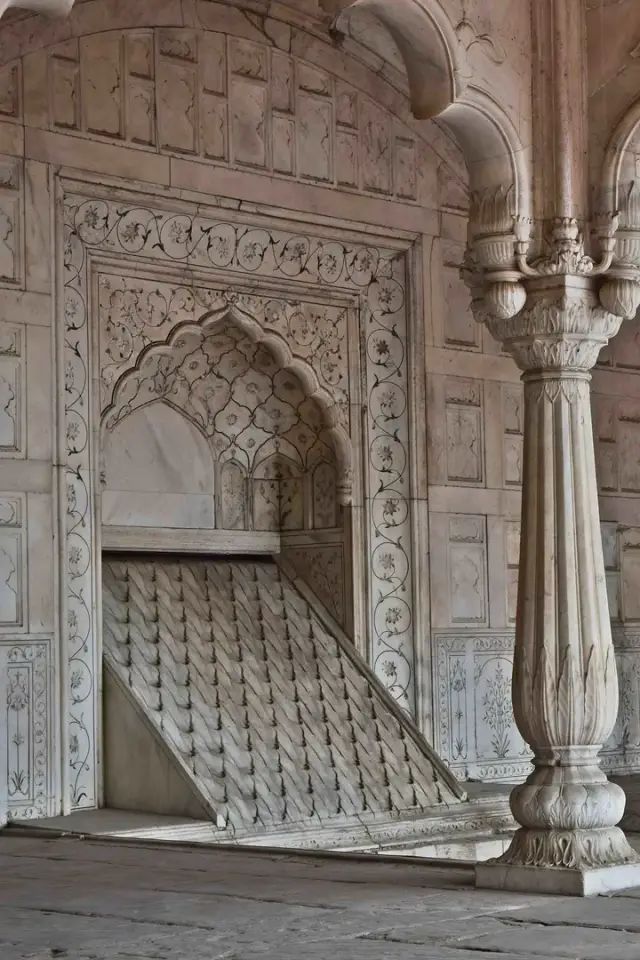

Among other buildings in Red Fort, there is an inclined fountain called salsabil.
The water flows out slowly through the small spout of the fountain, forming a small water flow on the slope, and providing a certain cooling effect through the temperature difference between the water flow and the building and evaporative cooling. Similar inclined fountains are widely found in buildings from North India to Spain, even in Pompeii sites.
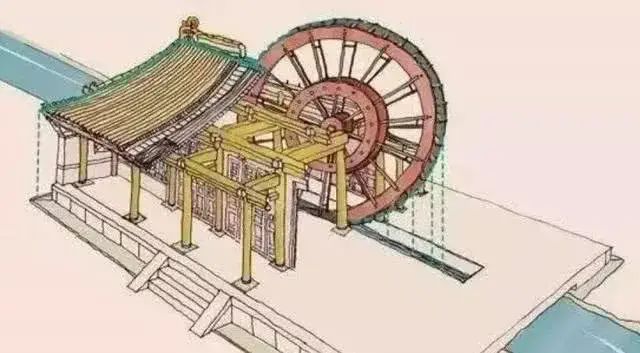
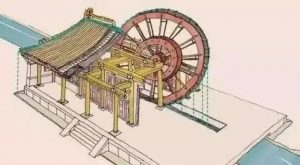
Similar buildings are also in China.
There is a building called Ziyu Pavilion. The principle is to use mechanical devices to transport water to the roof and reduce the temperature through water flow and water evaporation.
At that time, many rich people had cool houses in their homes, and water was transported to the roof by waterwheel to reduce the room temperature.
Ordinary families may not be able to afford to build fountains. How do they use evaporation for refrigeration?
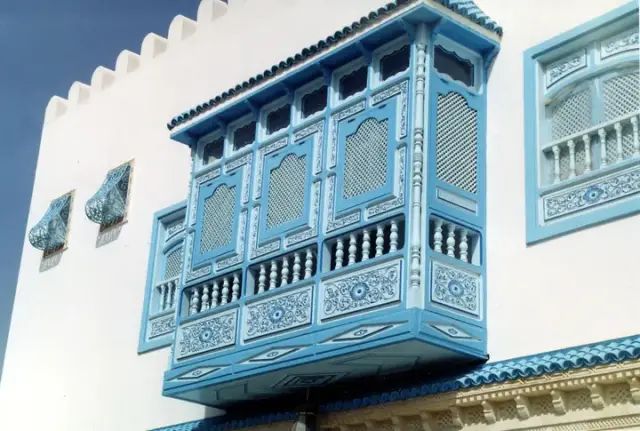

Many buildings in the Islamic world in the Middle East have a structure called mashrabiya.
Mashrabiya protrudes from the wall with many openings to capture the air flow and allow the air to pass through. Some water basins or tanks are placed inside for evaporation and refrigeration.
Mashrabiya replaces the windows and balconies in our buildings. In addition to cooling, it can also protect privacy.
Enhanced convection
The ancients came up with a lot of ideas in building structure to enhance evaporative refrigeration by strengthening convection.
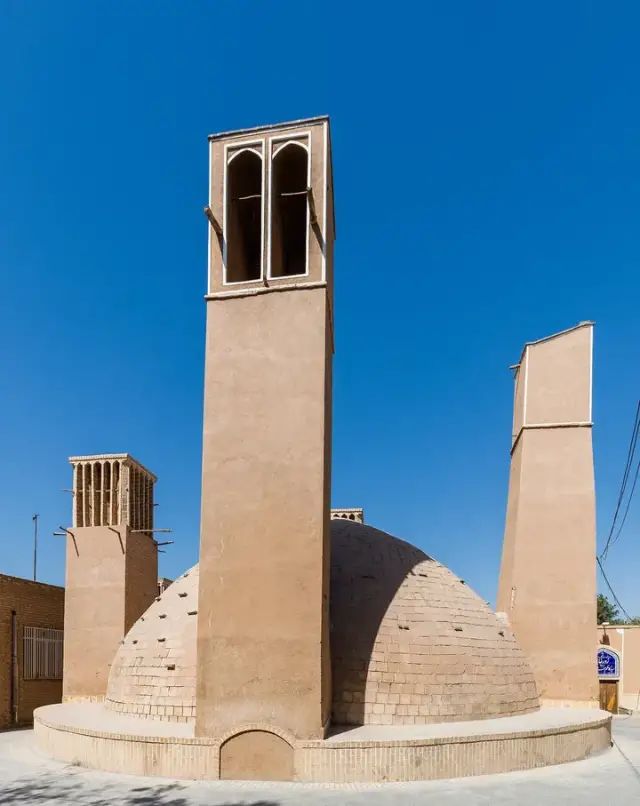

Auxiliary wind tower of AB Anbar reservoir in Yazd, Iran
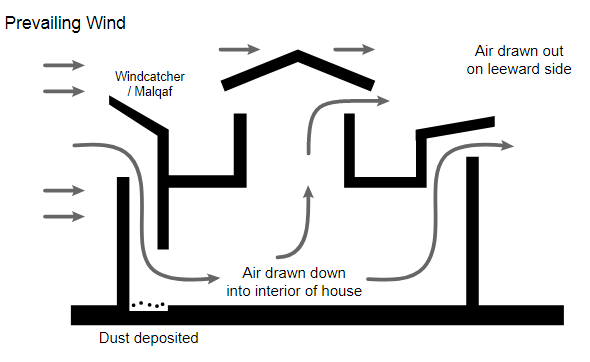
Schematic diagram of wind tower
Many buildings in the Middle East have a high wind tower, especially in Iranian buildings, wind tower is an important part. Using the temperature difference between the ground and high air, the wind tower can strengthen air convection. The higher it is, the stronger the convection will be. Combined with the attached pool, the wind tower can also accelerate water evaporation and strengthen evaporative refrigeration. In order to regulate the air flow direction and block the polluted air, the wind tower is additionally equipped with a filtering device, which can be switched on and off as required.
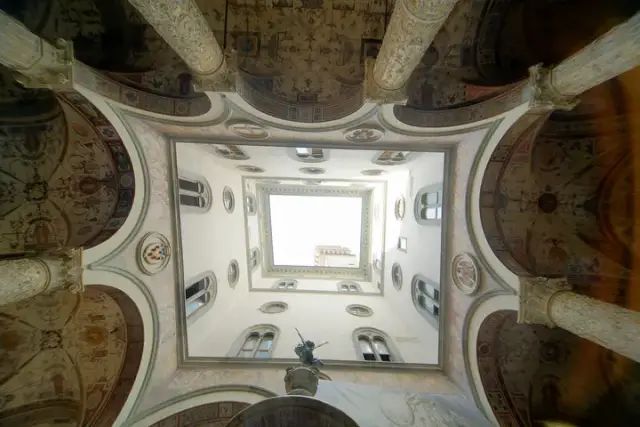

Elevated patio in ancient architecture of Florence
The building structure similar to the wind tower has appeared in ancient Egypt and Iran more than 3000 years ago, and there are similar structures in European buildings along the Mediterranean coast. Many ancient buildings in Italy opened a patio in the middle, with a pool or fountain under it.
The function of patio is similar to that of wind tower, which can strengthen air convection, and the pool can provide a certain evaporative refrigeration effect.
Wind tower is a passive ventilation device, and in China, people invented the earliest centrifugal fan to carry out active ventilation through mechanical power.

Fan car in The Exploitation of the Works of Nature
About 2100 years ago, Chinese invented fan cars, so long as the grain is put into a funnel, and the fan is turned by hand or foot, the shell can be blown open and the grain can be left. Fan structure in fan car is the ancestor of modern centrifugal fan. Using similar principles, Dingyan, a craftsman in Western Han Dynasty, invented a fan with 7 blades to push the blade to rotate by human force.
Geothermal coupling
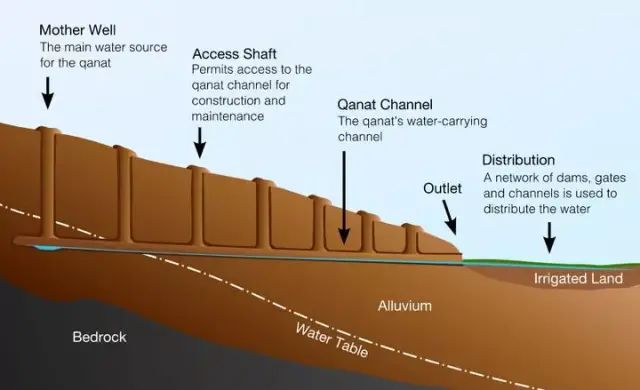
Karez
In Central Asia and the Middle East, there are many ditch systems that connect shafts with underground canals and store water through reservoirs. This kind of ditch is called Karez. It is generally believed that Karez was invented by Iranians more than 2000 years ago (but there are also views that Karez came from Xinjiang).
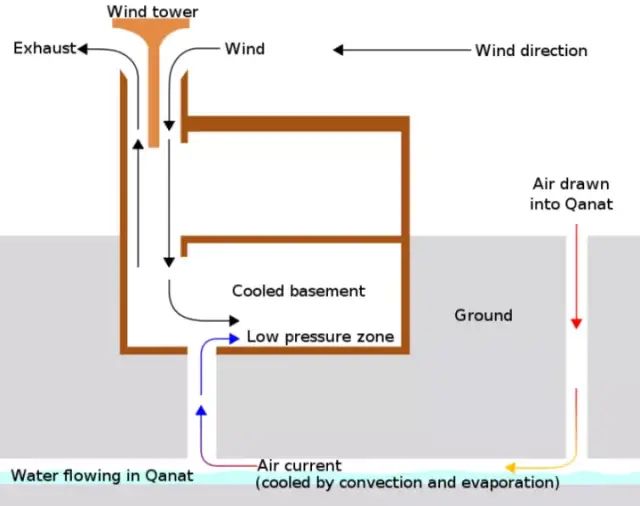
Dream linkage of Karez and wind tower
As mentioned earlier, because of the thermal insulation of the soil, the underground temperature is often lower than the ground in summer. Therefore, in summer, the water temperature in Kaner well is much lower than that on the surface. Using the temperature difference between the two, the water in Kaner well can be used to cool the buildings on the ground.
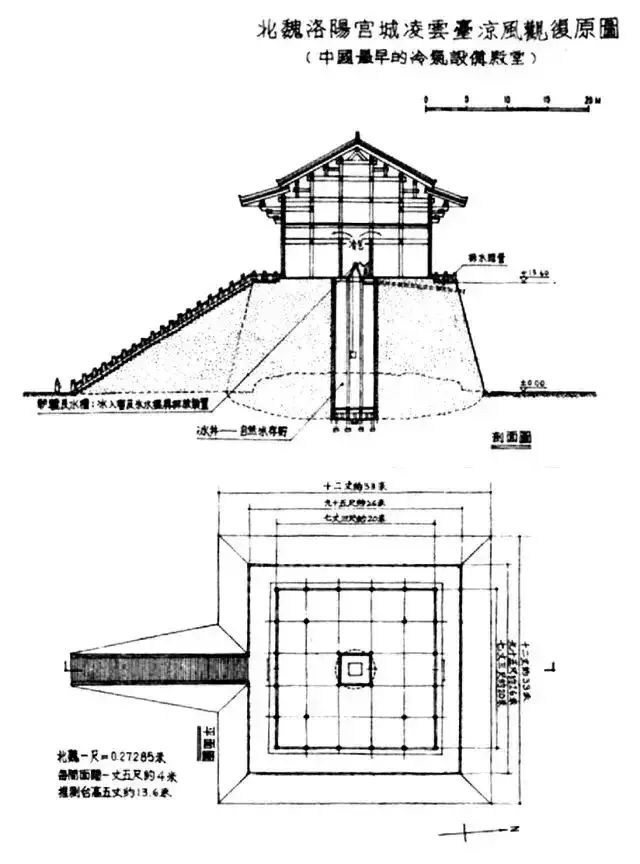
The cool wind view of lingyuntai, Luoyang City in the Northern Wei Dynasty, also used a similar principle to reduce the temperature through the convection of groundwater and air in the well.
Iran’s natural ice chamberāl, which can be said that the above-mentioned refrigeration means of the integration.
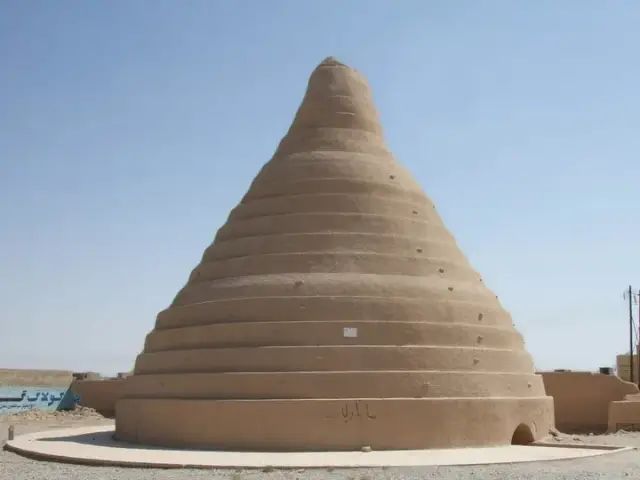

The outer wall of Yakhchāl is made of water-resistant and thermal insulation materials. The bottom wall is usually up to 2m thick, and the lower part is connected to the Karez.
The whole building is like an elongated steamed corn bread, with openings only at the bottom and top.
The structure of Yakhchāl is similar to that of the wind tower mentioned above, which can also strengthen air convection. In addition to providing geothermal exchange, the Karez connected below can further cool the water in the well after evaporation.
The Iranians began building Yakhchāl about 2400 years ago. Many existing Yakhchāl has a history of hundreds of years and can still be used today.
The temperature difference between day and night in the desert area of Iran is very large, and Yakhchāl is used refrigeration function, Iranians in Yakhchāl has a lot of ice in it, which can be used to produce cold drinks( According to some scholars, the earliest cold drink appeared in Ancient Iran, which should be a cold drink similar to ice shaving.)
Comments