
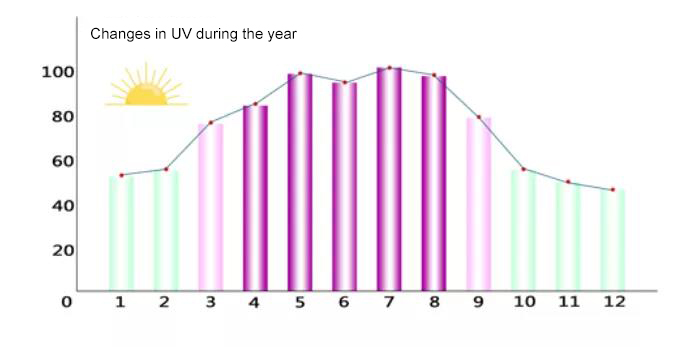
In half of May, even though you don’t feel very hot, the UV intensity at this time is already close to 90% of midsummer time.
When you go outdoors, you can feel the power of ultraviolet rays.
Although it can make people dark, ultraviolet light has many benefits to the human body. The season with the strongest ultraviolet rays of the year has arrived. What can we do to enjoy the sun without getting tanned?
When is the strongest ultraviolet light? (Subject to US Eastern Time)
Ultraviolet rays are not unique to summer sunlight. It exists every day, but its intensity is related to factors such as season, altitude, and latitude.
Strongest month
May to August
Starting from March each year, the intensity of ultraviolet rays gradually increases.
Ultraviolet rays have reached 90% of midsummer from March to April, and the peak period of ultraviolet rays throughout the year is from May to August. Even in winter, the amount of ultraviolet rays is 1/3 of that in summer.
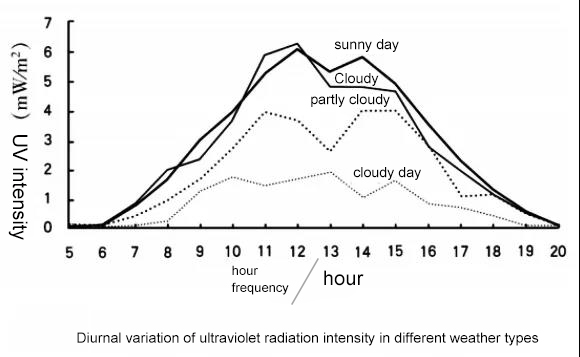
The strongest time: 10:00~16:00
The strongest ultraviolet rays are between 10 am and 4 pm, and it is almost negligible before 6 am and after 8 pm.
The strongest outdoor location: next to the glass exterior wall
Regardless of the surrounding environment, the strongest ultraviolet radiation is the glass exterior wall of the building, standing next to it in about 3 minutes can get erythema.
Strongest disguise: cloudy
On cloudy days, the sun also rises as usual, only sometimes covered by dark clouds. Clouds have a limited barrier to ultraviolet rays, and 90% of the ultraviolet rays can penetrate the clouds.
In addition, there are situations where the temperature is not high but the ultraviolet intensity is strong, so the “coolness” of the body feel cannot be used as a reference standard.
Ultraviolet rays, the body loves it but fears it
The main source of ultraviolet light in nature is the sun, and the body loves and hates it.
The skin is afraid of it
Darkening, wrinkles, cancer
Tan
After the skin is exposed to long-wave ultraviolet (UVA), melanin will begin to be produced within a few minutes. Ultraviolet rays (UVB) can cause severe sunburn such as erythema, blisters and even peeling after sunburn. Sunburn is an inflammatory reaction that often occurs after half an hour to several hours of sunlight exposure.
Wrinkle
Long-wave ultraviolet (UVA) can cause photoaging of the skin. According to Chris Griffith, a professor of Dermatology at Salford Royal Hospital in the United Kingdom, 75% of facial wrinkles are caused by sun exposure.
Cancerous
Ultraviolet radiation is an important factor leading to skin cancer. Sunburn is the prime culprit for the development of melanoma, and melanoma is the most dangerous of the three common skin cancers.
In addition, ultraviolet rays may also cause skin diseases such as polymorphic solar eruption and solar dermatitis.
Bones love it
Synthetic Vitamin D
Sunlight can help the body to synthesize vitamin D, can promote the body’s absorption and utilization of calcium and phosphorus, and is beneficial to bone health. Most of the vitamin D needed by the human body comes from the sun, and a small part comes from food. It can be said that the lack of vitamin D has a lot to do with the lack of sun exposure.
Breast
Benefit by the way
A new study published by Queen’s University of Canada in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives shows that compared with people who spend less than one hour in the sun a day in summer, people who spend more than one hour in the sun have a 16% lower risk of breast cancer. This conclusion applies to women of all ages, but the effect is more pronounced when young. This may be related to the synthesis of enough vitamin D from the sun.
In addition, insufficient sun exposure may increase the risk of diabetes and depression.
Bask in the sun, 6 steps to help you maximize your strengths and avoid weaknesses
Too much sun is worried about harming the skin, and too little sun is afraid of calcium deficiency (insufficient vitamin D synthesis). How to get sunburned so that you can fully enjoy the health benefits of sunlight while protecting your skin?
The answer is: apply sunscreen throughout the year. Sunscreen can filter out most of the ultraviolet radiation, but it will not block it completely. People who use sunscreen every day can maintain normal vitamin D levels while also protecting the skin.
The following 6 methods can help you bask in the sun scientifically.
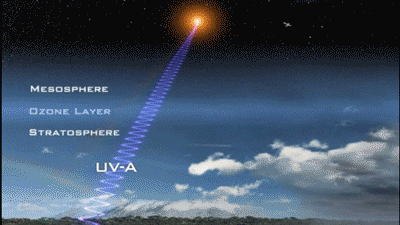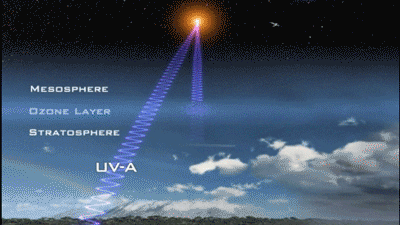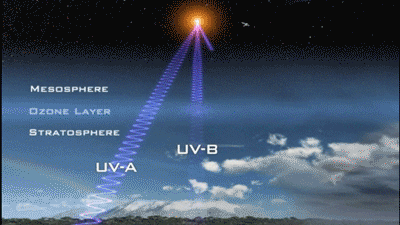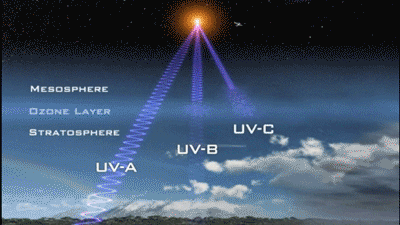
1. Avoid the strongest period of ultraviolet rays
In winter, the sunshine time is short and the ultraviolet intensity is weak, so you can choose to expose it at noon; in summer, if the ultraviolet rays are too strong, you should choose morning and evening, avoid 10:00~16:00.
If you want to find the best time to bask in the sun in a day, looking at the length of the shadow is a good way.
When the shadow is twice or more of the height, the UV index is the safest. You don’t need protection, so you can get a good exposure.
When the shadow is within the length of 1~2 times the height, it is safest to keep the sun for about 20 minutes.
When the shadow is shorter than the height, the ultraviolet rays may damage the skin within 30 minutes; if the shadow length is less than half of the height, the ultraviolet rays can damage the skin within 15 minutes.
2. About half an hour a day
Adults should be in the sun for 30 minutes to 1 hour a day; infants and children can be appropriately shortened to 15 to 30 minutes due to their delicate skin; the ability of the elderly to synthesize and use vitamin D is reduced, and the time can be appropriately extended , but not too long at a time.
3. Go outdoor
The health benefits of sunlight are a comprehensive effect, that is, the superposition of receiving sunlight and going out. In addition to helping the body to synthesize vitamin D, outdoor activities can also improve mood, which is an important part of maintaining health.
4. Eat more fruits and vegetables after sun
Eat more fruits and vegetables after sun drying. Fruits and vegetables are rich in vitamin C. Many studies have confirmed that supplementing with vitamin C can inhibit melanin production and prevent sunburn.

5. Supplement vitamin B3
A study published in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2015 showed that oral vitamin B3 can reduce the risk of new non-melanoma skin cancers and actinic keratosis in high-risk patients.
After sun exposure, it is recommended to supplement foods rich in vitamin B3, such as animal liver, chicken breast, salmon, pork, avocado, mushrooms, etc.
6.3 types of people double sun protection
Going to the beach will receive a lot of sunlight in a short period of time, which is easy to cause sunburn, so you should do sunscreen work.
People living in high-altitude areas such as Qinghai and Tibet, as well as those who have been engaged in outdoor work for a long time, must pay attention to sun protection.
People with photosensitivity and those who are taking photosensitivity drugs such as sulfonamides and quinolones are best to keep sunscreen strictly.
More exposure to the sun represents an active, open and sunny lifestyle, which will play a very active role in the prevention and treatment of many diseases. Even in the summer, please don’t refuse the sun, and learn to be a healthy person who can bask in the sun.
Comments