
Do you think pterosaur is dinosaurs? In fact, it is just a kind of flying reptile. So, who is the dinosaur that can fly? Let’s take a look!
Archaeopteryx is not a bird
Many people think that the ancestor of bird is Archaeopteryx because it has wings and feathers and its head resembles a bird. But it is not the ancestor of bird, nor is it a bird, but a small theropod dinosaur.
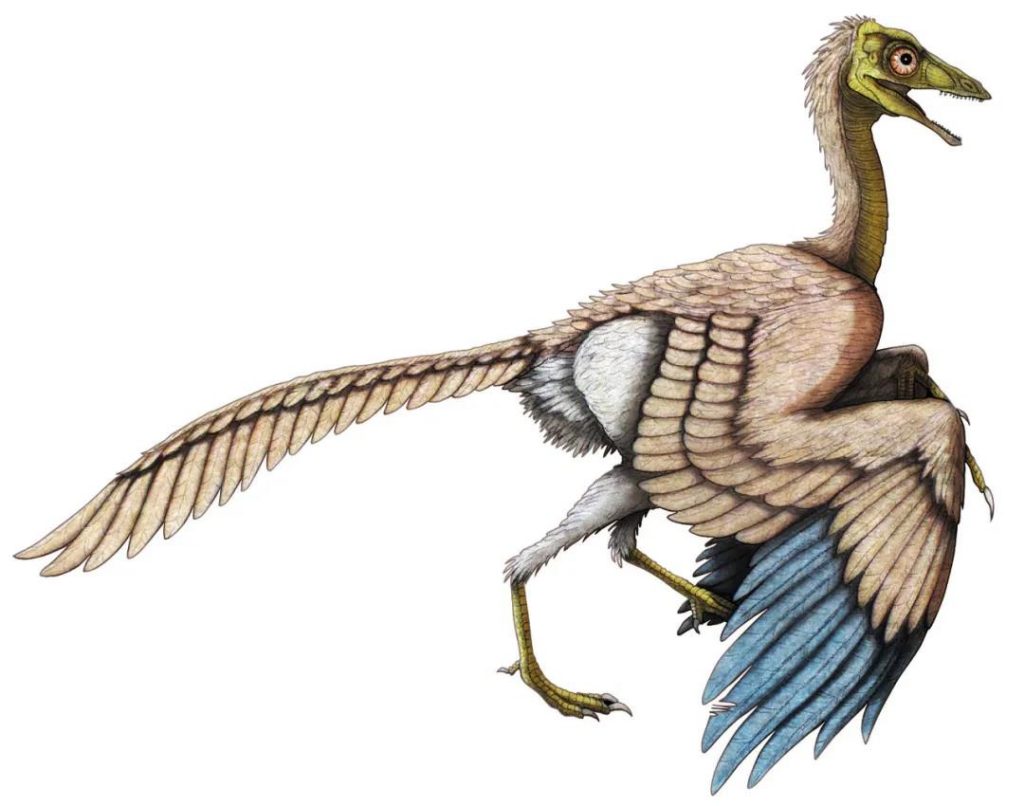
Archaeopteryx
Location: Germany
Living time: Jurassic period about 150 million years ago
Archaeopteryx’s forelimbs have asymmetrical feathers, and it can use the air pressure difference generated from the upper and lower feathers to make the limbs obtain a lifting force to achieve a certain flight. However, many parts of Archaeopteryx’s body are still immature. For example, modern birds have barb-shaped wings and feathers, but Archaeopteryx’s feathers do not; the palms of its forelimbs have not yet fully healed, and the fingertips have claws exposed. Therefore, Archaeopteryx can only fly short distances, short periods of time, and low altitude.
The true ancestor of birds- Confuciusornis
Scientists believe that the Confuciusornis is the ancestor of birds. The Confuciusornis is very similar to Archaeopteryx in size, with a body length of about 50 cm and a weight ranging from 0.2 to 1.5 kg. But Archaeopteryx still has a tooth structure, while Confucius’s teeth have degenerated, approaching modern birds; and it has the earliest horny beak.
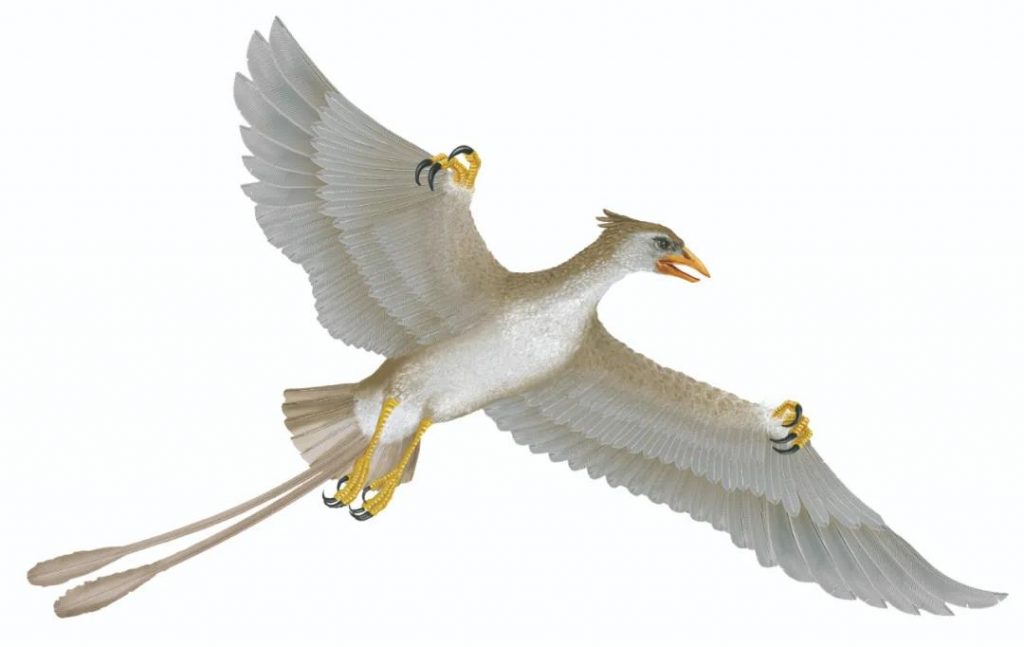

Confuciusornis
Location: Liaoning, China
Living time: the end of the Cretaceous period 120 million years ago
The feathers of the Confucius bird’s wings are very long, even longer than those of modern birds. Some of the feathers have a barb-like structure, which helps the feathers lock to form a plane to beat the airflow; it also has a pair of slender tail feathers. , The shape of the wings also tends to be consistent with the birds in the dense forest. All this shows that Confucius Bird is likely to have stable and flexible flight capabilities.
Four-winged Microraptor
Microraptor is one of the smallest known dinosaurs in the world, measuring only 40 to 80 cm in length and weighing only about 1 kg. They are covered with a thick layer of feathers, with long barb-like feathers on their forelimbs, hindlimbs, and head. They are the first four-winged dinosaur discovered so far, and all four wings can help fly.
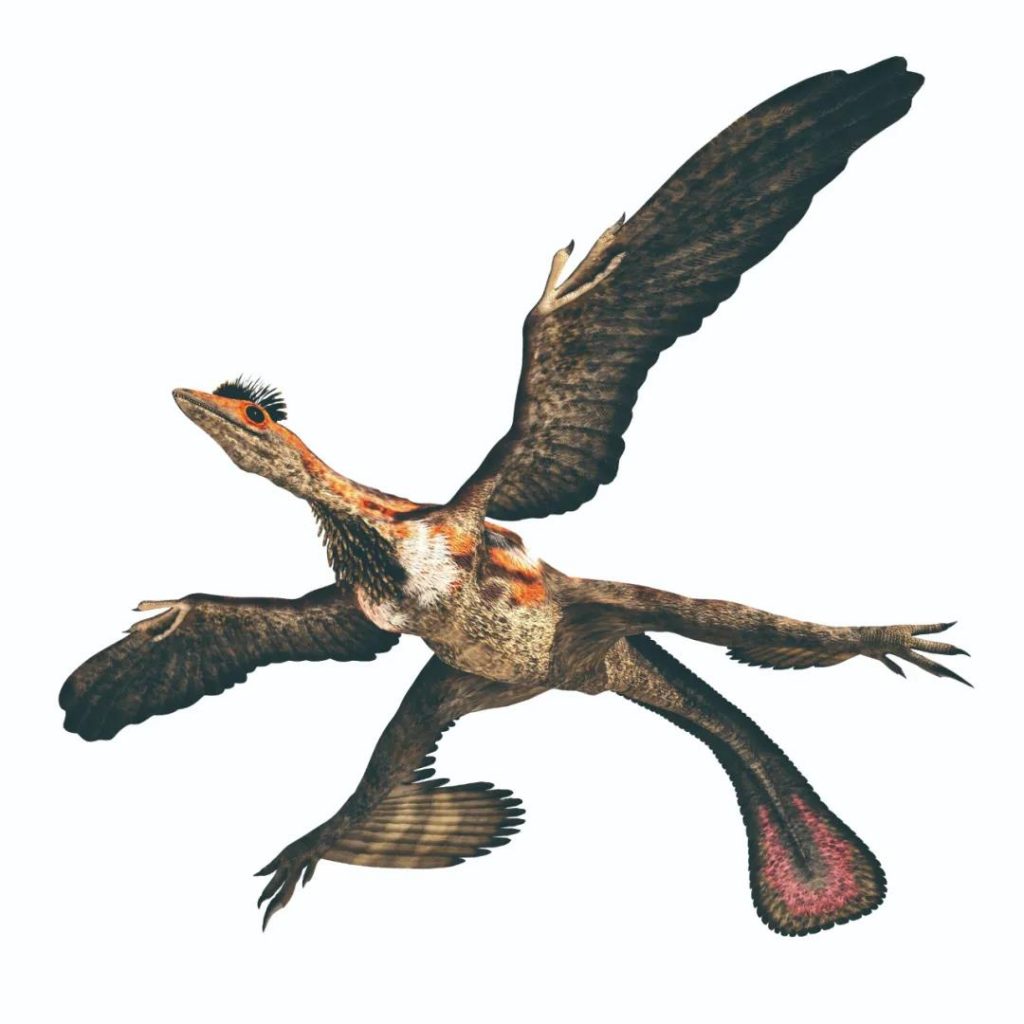

Microraptor
Location: Liaoning, China
Living time: 130 million years ago to 126 million years ago at the end of the Cretaceous
According to the analysis of biologists, Microraptor may inhabit trees and can glide freely in the forest. It was also a carnivorous dinosaur, feeding on other smaller dinosaurs or insects, and occasionally carrion.
Jeholornis that loves to eat seeds
Jeholorniss are also small in size, reaching 75 to 85 cm in adult body length; they have a very slender tail, composed of more than 20 tail vertebrae, and the feathers at the tip of the tail are sparsely fan-shaped. The forelimbs of the Jeholornis are longer than the hind limbs, the muscles are stronger, and the shoulder blades (the bones that control the flapping of the forelimbs) are also more developed, indicating that the Jeholornis is likely to have a certain flying ability.
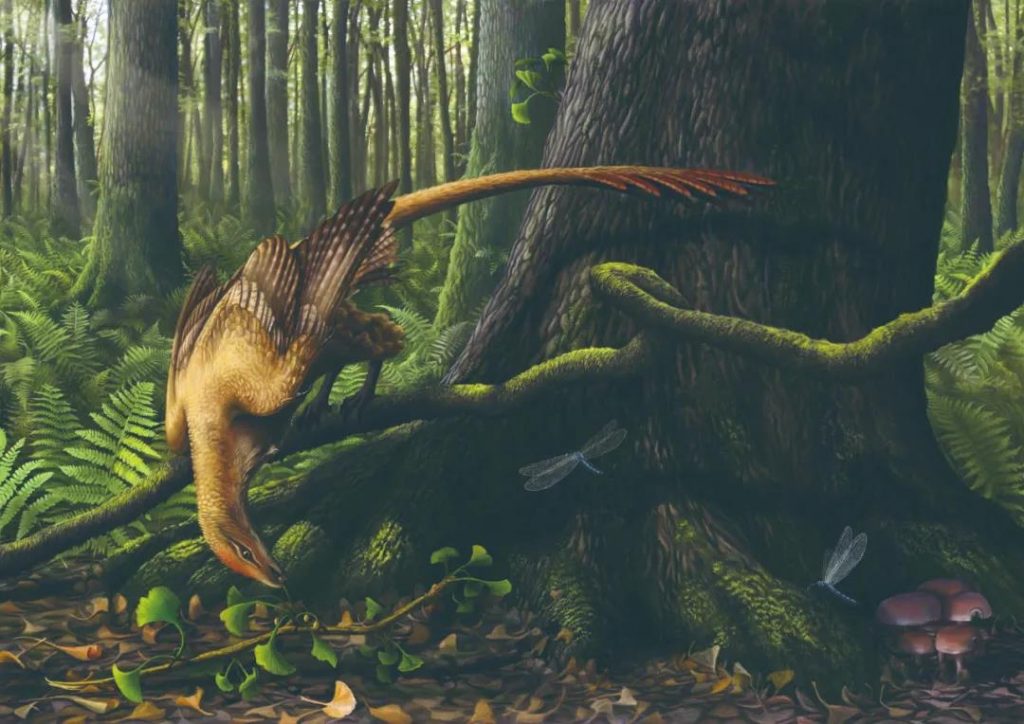

Jeholornis
Location: Hebei, China
Living time: the end of the Cretaceous period 122 million years ago
In addition, scientists found a large number of plant seeds in the stomach of a Jeholornis fossil, indicating that Jeholornis feeds on plant seeds.
Sinornithosaurus with Long Venom Gland
The length of the Sinornithosaurus is about 90-120 cm in length. Their skeletal structure is very similar to that of Archaeopteryx, and their forelimbs and hind limbs are feathered, and they can use their wings to achieve gliding.
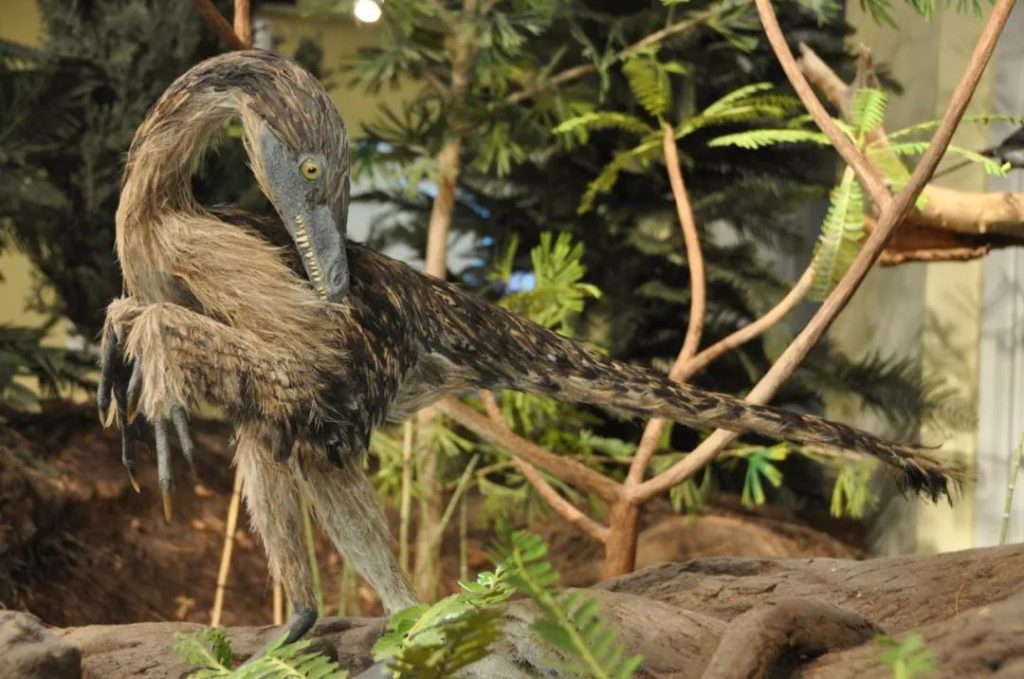

Sinornithosaurus
Location: Liaoning, China
Living time: the end of the Cretaceous period about 125 million years ago
Sinornithosaurus is a carnivorous dinosaur. They are likely to glide down from the tree behind their prey and launch a surprise attack. At the same time, they use a special weapon-the poison gland located in the upper jaw. Inject into the prey, causing it to fall into paralysis or even shock.
Comments