
For many people, the word “weight loss” is often on the lips, but no action is seen. Or because of various reasons, the more you lose weight, the more you get fatter, and you have to give up in the end.
A new study published by Loughborough University in the Public Science Library Medical Journal found that the longer you are obese, the higher your risk of cardiovascular and metabolic diseases.

Why should I lose weight early?
The longer you get fat, the worse your blood vessels
In order to clarify the relationship between cardiovascular disease and the degree and duration of obesity, the research team at Loughborough University in the United Kingdom selected 20,746 subjects between the ages of 10 and 40, and collected the subjects’ body mass index and risk factors for cardiovascular and metabolic diseases ( Including blood pressure, cholesterol and glycosylated hemoglobin levels, etc.), analyze the age of obesity, obesity duration and severity.
The severity of obesity is determined by body mass index (BMI).
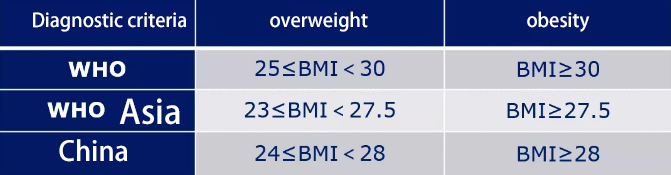
Body mass index (BMI) = weight/height square (unit: kg/㎡)
It was found that the duration of obesity was related to the risk factors of cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. These risk factors include systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, good cholesterol, and glycosylated hemoglobin.
The longer the obesity lasts, the worse the value of risk factors for cardiovascular and metabolic diseases.
Compared with people who are not obese all year round,
The level of glycosylated hemoglobin in people who are obese for less than 5 years will increase by 5%;
The level of glycosylated hemoglobin in people who are obese for 20 to 30 years will increase by 20%.
Fat on the waist, blood vessels are more dangerous
According to a study published in the European Heart Journal, women with the most fat or “apple” shape have a 91% higher risk of cardiovascular disease than women with the least fat.
The relationship between body fat, lean tissue and anthropometric indicators
People with a thick waist will have thicker subcutaneous fat, which will dilate capillaries, increase blood circulation, and increase cardiac output. Long-term overload will induce left ventricular hypertrophy and increased blood pressure.
Waist-to-hip ratio = waist circumference ÷ hip circumference
To measure the waist circumference, stand with your feet 30 cm apart, and the measuring part should be flat to the umbilicus. Use a soft ruler to stick to the skin, but not to compress it.
Normal male waist circumference <85 cm, female waist circumference <80 cm.

The World Health Organization recommends that a waist-to-hip ratio of more than 0.90 for men and 0.85 for women can be diagnosed as central obesity.
In addition to cardiovascular disease, the researchers also pointed out that higher abdominal fat levels are also related to various metabolic disorders, such as insulin resistance, dyslipidemia and inflammation.
Fat-loss plan for all ages
Although different groups of people have different fat-reduction programs, it is simply to pay attention to diet + exercise. Experts formulate a scientific heart-care and fat-reduction plan for the three groups of people, and follow suit to benefit both body weight and heart.
Young and middle-aged
Eat dynamic balance, pay attention to decompression
1. Adults’ diet should follow the principle of “full breakfast, good lunch, and less dinner”, less take-out food, steaming, boiled, and stewed cooking, and less oil, salt and sugar. Replace the snacks at hand with nuts, yogurt, etc., and change yourself to a smaller bowl.
2. People who sit for a long time in the office should do more thin waist and abdomen movements, such as plank support and hip bridge. You can practice squatting, side-lifting, etc. between work. Put a weight scale in the bedroom and measure it every morning and evening.
3. Take time to do more outdoor sports, exercise at the same time to reduce stress and adjust your heart, and exercise together is also a good choice. Running and brisk walking are recommended, 3 to 5 times a week, 30 minutes each time.

Elderly people, eat small meals more often, exercise to the best of your ability
1. The middle-aged and elderly people maintain a fat body to help regulate immunity and delay aging. For the elderly, the body mass index between 18.5 and 25 is the most suitable. What needs to be emphasized is that it is best not to have more fat, but more muscle.
2. Elderly people with chronic diseases such as “three highs” should adopt small and frequent meals in their diet. Eat 4 to 5 meals a day, each with a full seven points, and increase the ratio of miscellaneous grains and potatoes to the staple food.
3. Elderly people should exercise according to their ability and pay attention to warm-up and stretching before and after exercise. During exercise, the heart rate can gradually reach the maximum value, that is, 220 minus 60%~85% of the age. If you experience difficulty breathing, dizziness, or rapid heart rate, you should stop exercising immediately.
Teenagers, while consuming, replenish
Infancy weight gains quickly, reaching 2 times the birth weight at 3 months, and 3 times the birth weight at 12 months.
Before and after the school age, the weight development slowed down, and the average body weight increased by about 2 kilograms per year.
At puberty, development has entered a period of rapid growth.
1. Good weight control is an important factor for young people to secrete growth hormone. According to the recommendations of the Chinese Nutrition Society, daily intake during growth and development: a glass of milk, an egg, two walnuts, two fruits, three meats, and three vegetables , a handful of grains.
2. Stay away from fattening foods, such as candies, biscuits, potato chips, jelly, etc., eat less fried foods, and try to drink pure milk.

3. Get enough sleep for 8 hours a day and get more sun. 1 hour of outdoor exercise a day, such as ball games, skipping rope, etc., can increase bone strength and consume excess calories.
Comments