
The earth has only one natural satellite, the moon. However, there are more and more artificial satellites orbiting the earth.
Earth surrounded by stars
Artificial satellites are carried above the earth by rockets and orbit the earth under the action of gravity and inertia.
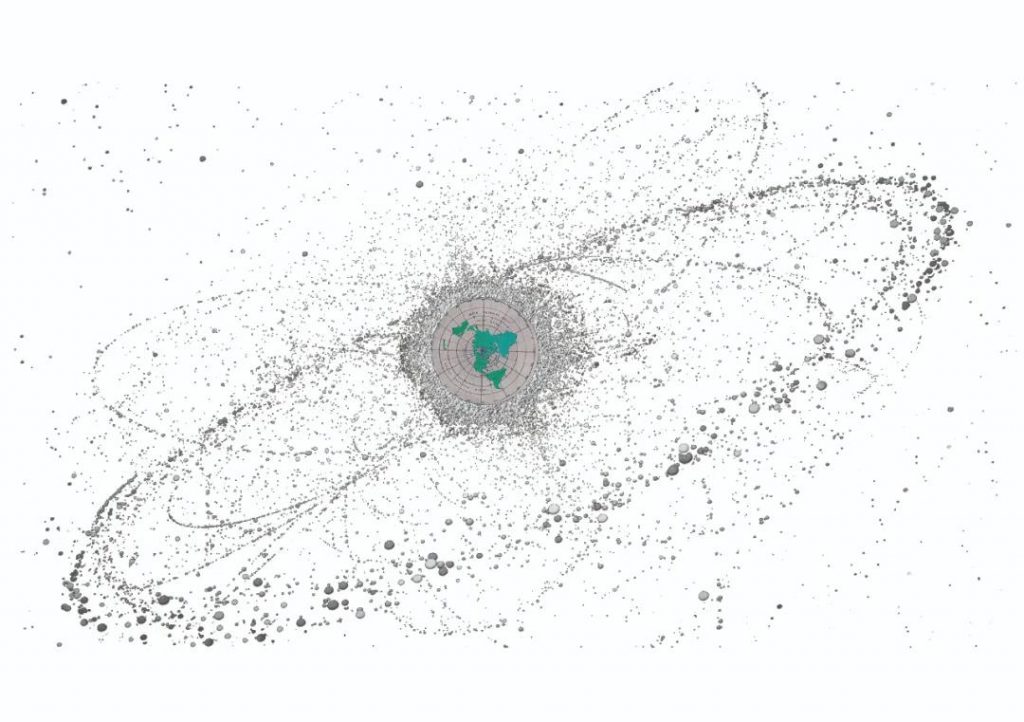
Saturn has 82 moons, the planet with the most moons currently known. But if you count artificial satellites, the Earth is way ahead – as of January 2021, there were 3,372 satellites in orbit; more than 6,000 if you count those that have been deactivated but not dropped .
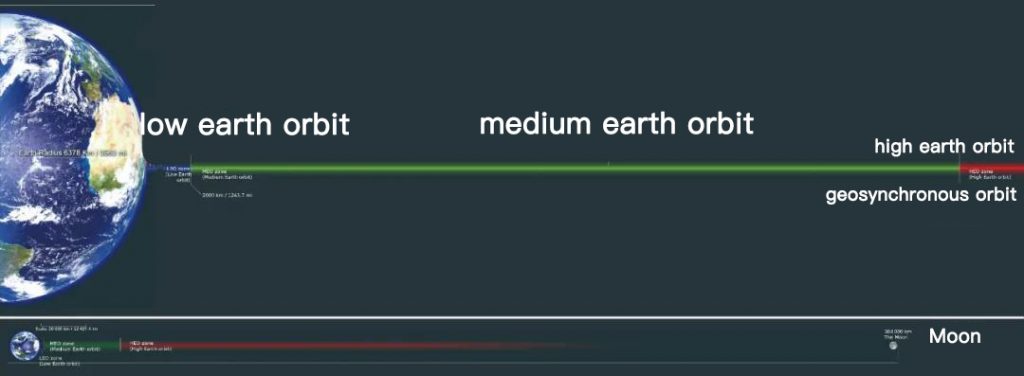
Satellite highway is divided into high and low levels
The signal is transmitted between the artificial satellite and the ground in the form of electromagnetic wave. Just as the closer the mobile phone is to the router, the stronger the WiFi signal is, the closer the satellite is to the earth, the better the quality of signal transmission is, so communication satellites are generally in a lower orbit; When the satellite is far away from the earth, the signal quality becomes worse, but the coverage is wider, so the relay satellite is in a higher orbit, which is convenient for remote control of other satellites.
Satellites need electricity to operate. It has a battery inside and a huge solar panel outside, which uses sunlight to generate electricity. Some satellites also have fuel tanks and thrusters that can be propelled by burning chemical fuels.
The role of satellites is varied
Artificial satellites sound very far away, but in fact, they are silently helping mankind all the time, from daily travel to exploring the universe.
Travel navigation
Map navigation is an essential application on everyone’s mobile phone today. It is not only used in strange places, but also used in familiar places. People sometimes let navigation software plan a more convenient and fast new route for themselves.
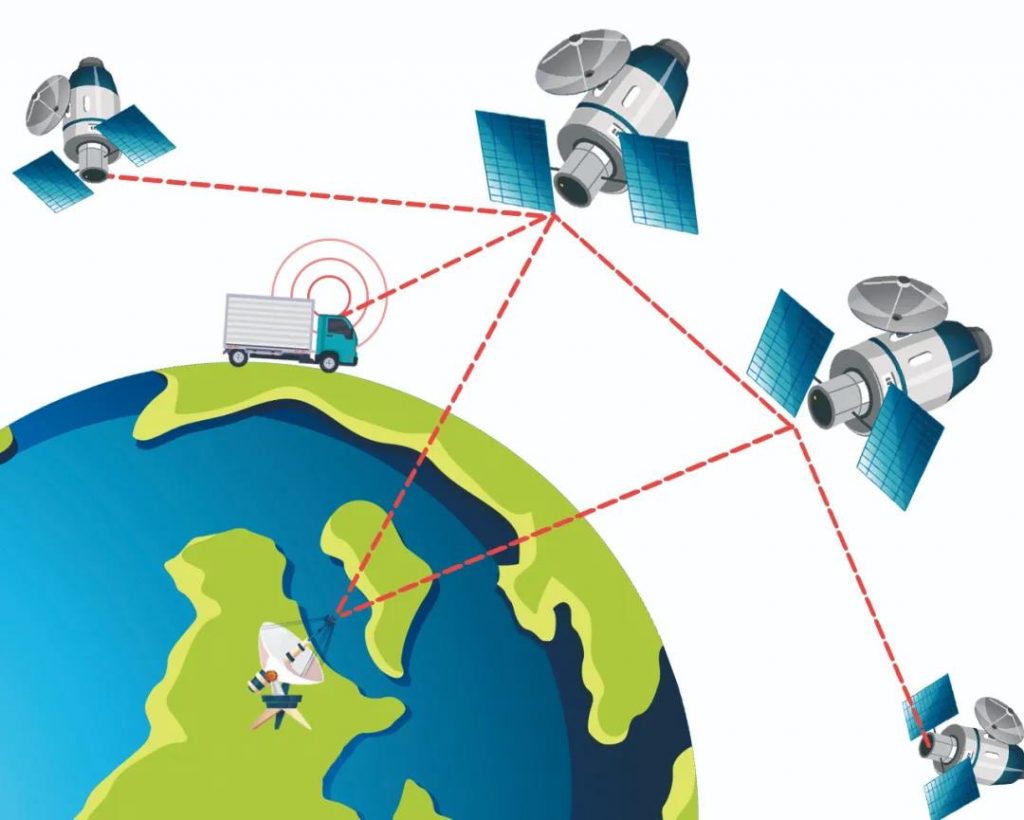
Navigation services rely on navigation systems composed of dozens of satellites in space, such as global positioning system (GPS), Beidou satellite navigation system, etc. they can quickly find the location of mobile phones and send location information back to mobile phones. Aircraft and ships also need similar software to locate.
Forecast weather
Meteorological satellites overlook the earth, conduct 24-hour continuous weather monitoring all over the world, and shoot clouds, ice and snow, fire, smoke and so on. Meteorological workers analyze these photos and become the weather forecast we see every day.

Explore universe
Space telescopes also belong to man-made satellites, such as the Hubble telescope, which gives us a magnificent picture of distant celestial bodies.
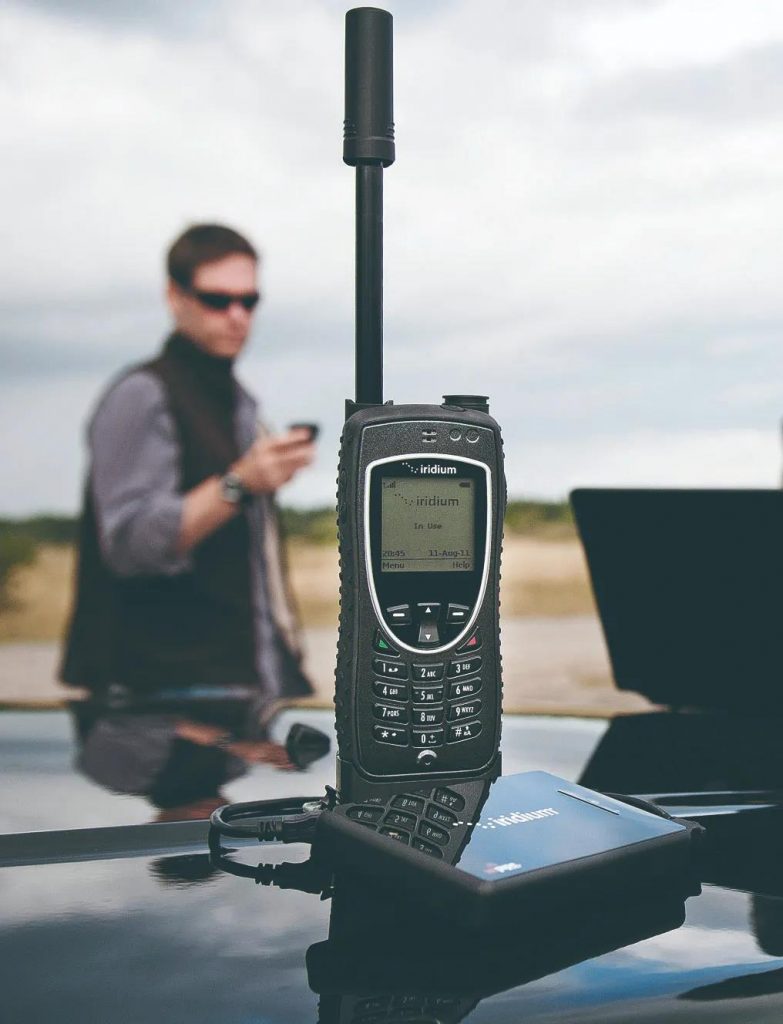
Satellite telephone
Usually, when we use a mobile phone, the mobile phone signal will be transmitted through the base station. But in inaccessible areas, such as desert and sea, there is no base station and mobile phone has no signal at all. At this time, people need to use satellite phones to contact the outside world and transmit signals by satellites.

Spy satellite and killer satellite
Spy satellites secretly take pictures of the ground of other countries and steal military secrets. Some people have also proposed to install laser weapons on satellites to destroy enemy missiles or spacecraft; but laser weapons require a lot of energy, and it is difficult for people to move such a huge energy supply equipment into space. This kind of killer satellite is only a fantasy at present.

Without satellites
If one day, all the satellites disappear, our life will be a mess.
First, paper maps became a must when going out, planes would get lost in the clouds, and sailors had to rely on compasses and stars to find their way. The weather forecast will become a “no prize quiz”. Disasters such as typhoons and sandstorms will appear and disappear, causing people to be caught off guard; once a disaster occurs, people in remote areas will have nowhere to ask for help…

You also can’t surf the Internet normally, because the Internet has strict network protocols, and you need to rely on satellites to calibrate the time around the world, so that the time can be accurate to send and receive information. Without satellites, the network would be seriously out of order.
Garbage surrounds the earth
We can’t live without satellites, but too many satellites can cause trouble.
Debris from scrapped satellites and rockets can become space junk, and even a tiny screw can knock out a satellite’s solar panels. Today, there are hundreds of millions of pieces of space junk floating around the Earth.
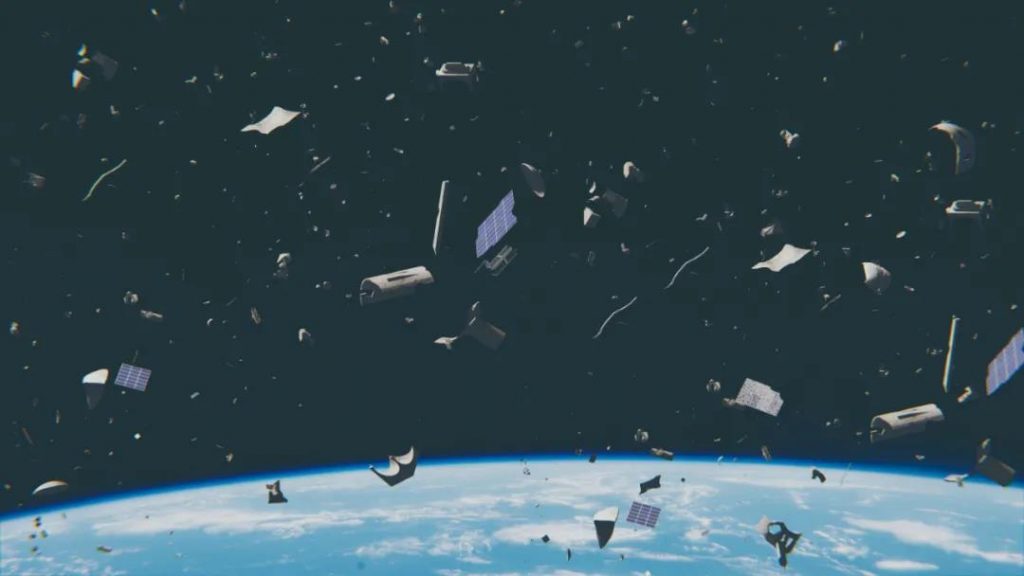

Satellites will also interfere with the field of view of ground-based astronomical telescopes, and some scientists even mistake passing satellites for newly discovered celestial bodies, causing an Oolong event.
Watch out for satellite crashes
In February 2009, two artificial satellites collided at a high speed of 11,700 m/s, and both perished on the spot and disintegrated into thousands of pieces. In 2012, a piece of debris passed by 120 meters away from the International Space Station. In space, this is equivalent to passing by. For safety, the astronauts in the space station also took refuge in the Soyuz spacecraft.
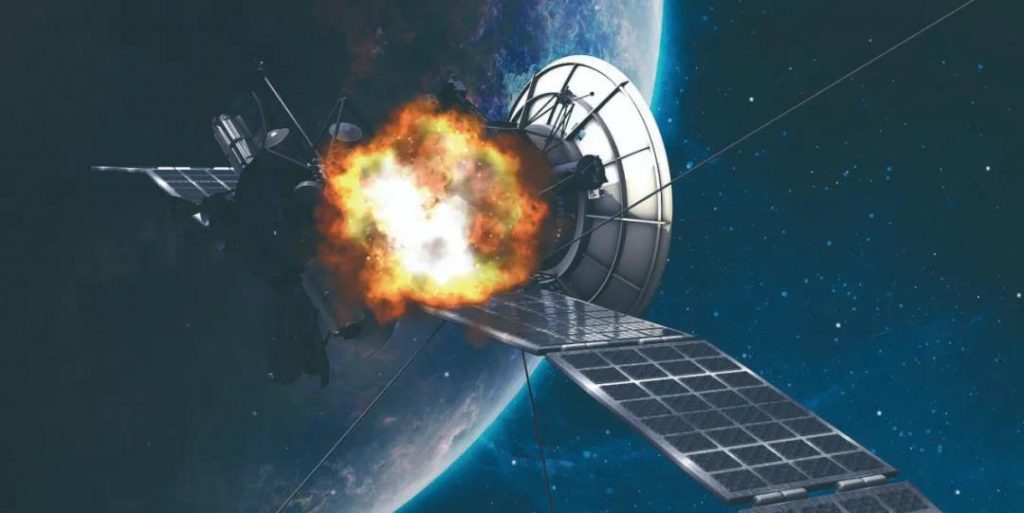

Since there is currently no international treaty to limit space junk, a large number of satellites are launched into space every year, resulting in a continuous increase in space junk. In the future, satellites are likely to collide again. To make matters worse, if one satellite crashes, its debris may hit other satellites, causing a chain of car crashes.
In order to avoid a tragedy, scientists racked their brains and came up with a variety of solutions.
space traffic police
Today, NASA’s space surveillance network keeps an eye on satellites and tens of thousands of pieces of space junk, recording their flight paths. As soon as an object gets too close, the surveillance network sends an alert, alerting nearby spacecraft to perform “evasive maneuvers,” fine-tuning their flight paths to avoid a collision.
Where do satellites go after decommissioning?
Some satellite operators plan to accelerate satellites when they are nearing end-of-life into “graveyard orbits” well above geosynchronous orbits, which would avoid the vast majority of in-service satellites. Others go into lower “disposal orbits” and burn up in the atmosphere.
space cleaning vehicle
Scientists are researching and designing a variety of “cleaner vehicles” to collect end-of-life satellites and space junk without propulsion capabilities.
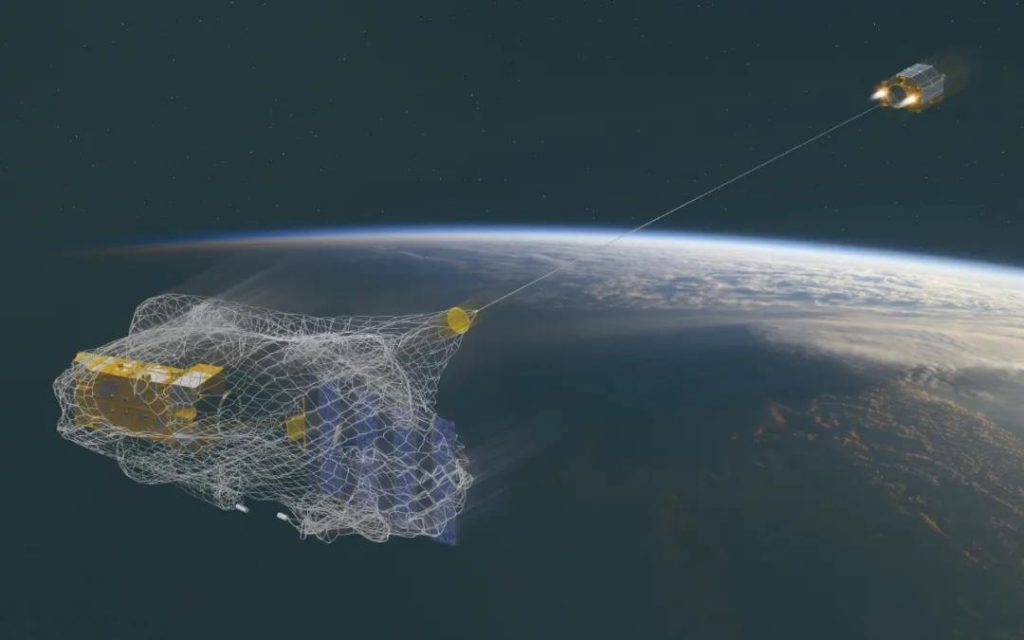

In 2016, Japan sent a device to the international space station to try to pull space debris out of orbit with a rope, but failed.
The European Space Agency plans to launch a man-made satellite with a mechanical arm in 2025. It can catch the abandoned satellite in orbit and take it into the atmosphere to burn it.
Comments