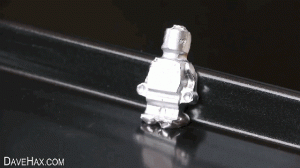
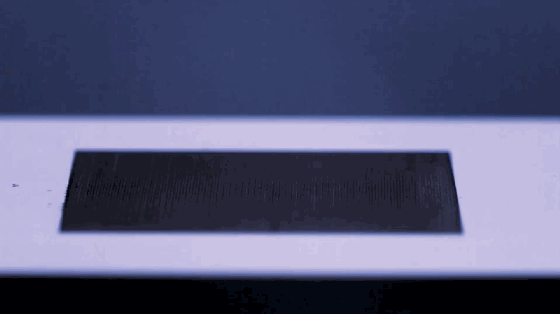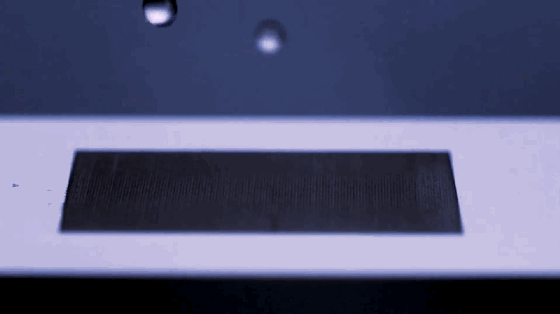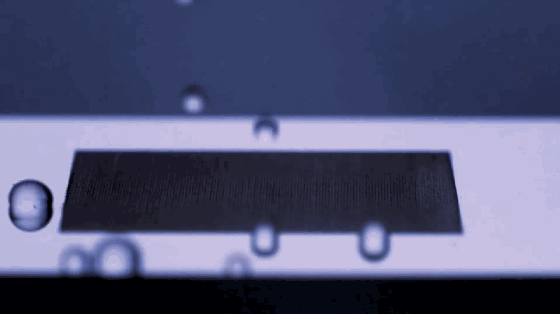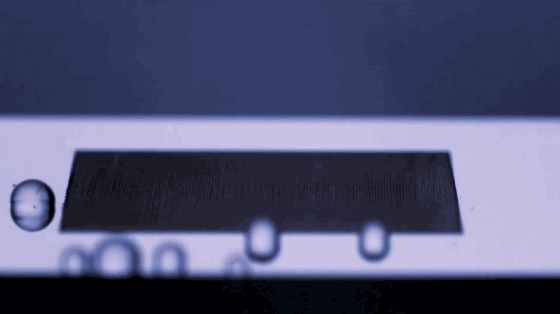
1. Superhydrophobic materials

Superhydrophobic material is a new type of material. Its surface has special micro-nano structures, and there are substances with low surface energy on these structures, so it is difficult for water to adhere to its surface. China has made outstanding contributions to the research and application in this area, and has reached the international leading level.
2. Nitrogen Triiodide

Nitrogen triiodide is one of the most explosive substances on the earth. It is a deep red solid, weak in stability and very sensitive. In a dry state, any slight contact may cause a violent explosion. This feature makes it often used in some magic or special effects performances.

3. Hydrogel

Hydrogel is a gel with water as the dispersing medium. It is a polymer network system, soft in nature, able to maintain a certain shape, and able to absorb a large amount of water. As a material with high water absorption and high water retention, hydrogels are widely used in many fields, such as drought resistance, cosmetics, agricultural films, construction, petrochemicals, mining, food preservation or thickening, and medical and drug carriers.

4. Shape Memory Alloys

Shape memory alloy is a special kind of alloy. Under some conditions, the shape changes and changes to the original shape after heating. At present, scientists have found more than 50 kinds of alloys with shape memory effect, which are widely used in aerospace, mechanical electronics, biomedicine and other fields.

5. Gallium

Gallium is a gray blue or silver white metal. Its melting point is very low, only 29.8 ℃, so it will melt in hot water, even in the palm of human hands. It is widely used in semiconductor industry, solar cells and other fields. It is a very important strategic resource.

6. Aerogels

Aerogel is the world’s least dense solid. The lightest aerogel density is only 0.16mg/cm. ³( 2013). Similar to the hydrogel in the front, aerogels are porous network structures, which are mainly gas, so they are very light.

7. Magnetic plasticine

Nothing special. It’s just plasticine mixed with magnetic particles, but it’s full of spirituality like life. The interaction with magnets is very interesting.
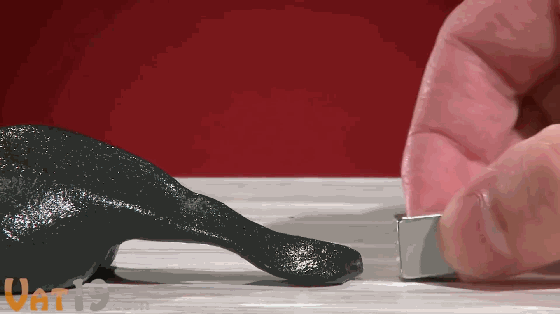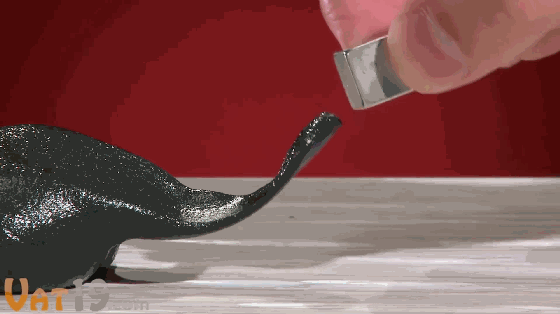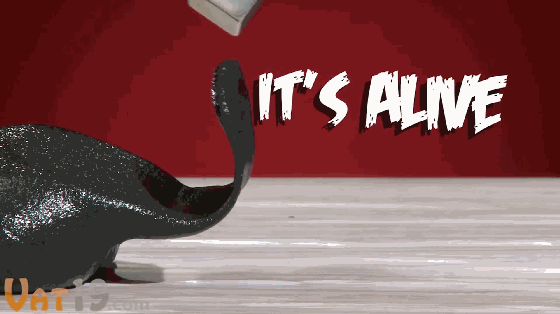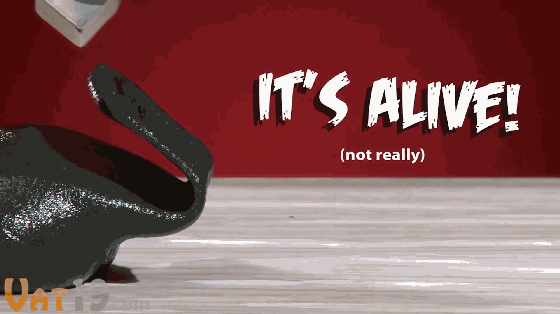
8. Magnetic fluid
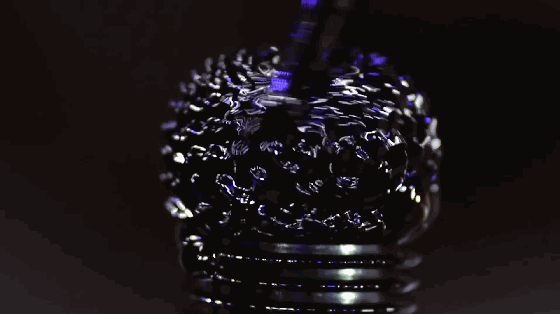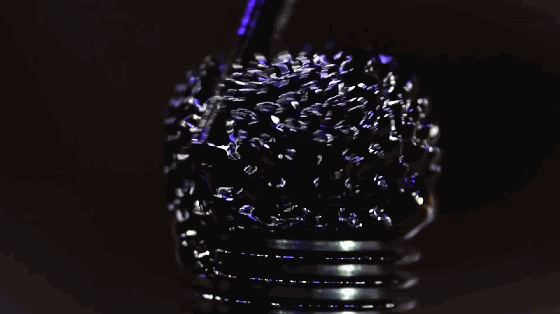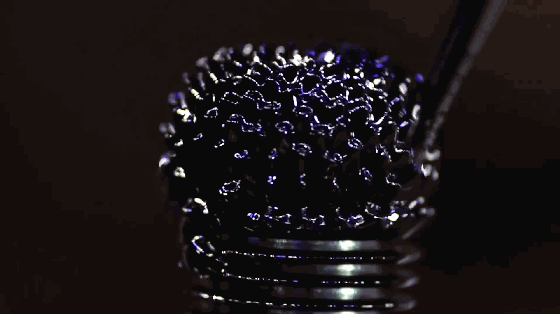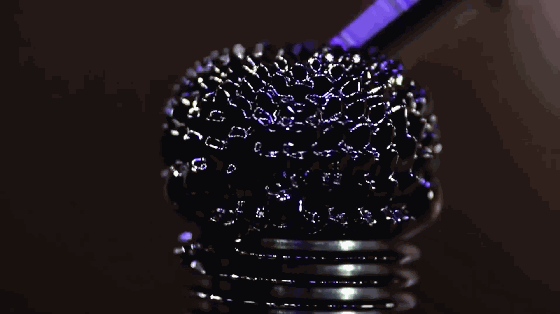
Magnetic fluid is a colloidal suspension liquid, also known as magnetic fluid or magnetic fluid. It is formed by ferromagnetic ultrafine particles with an average diameter of 10 nm, adsorbing a layer of surfactant on the surface and stably dispersing in base liquids such as oil and water. As a new type of liquid functional material, magnetic fluid has both the magnetism of solid materials and the fluidity of liquid materials, and has many novel properties and applications.
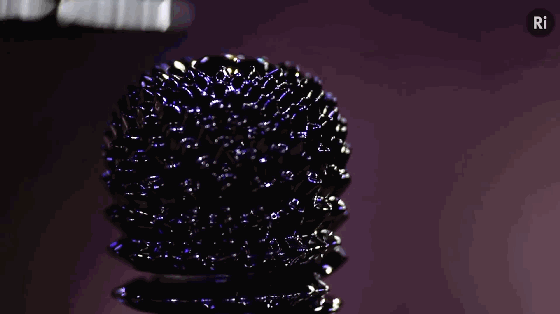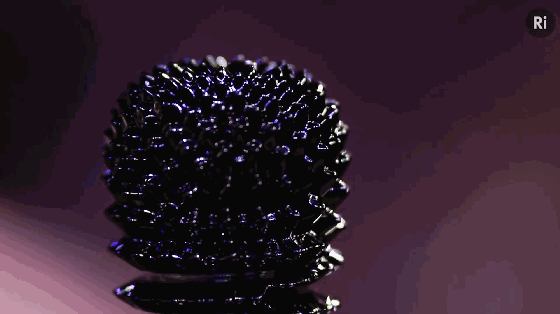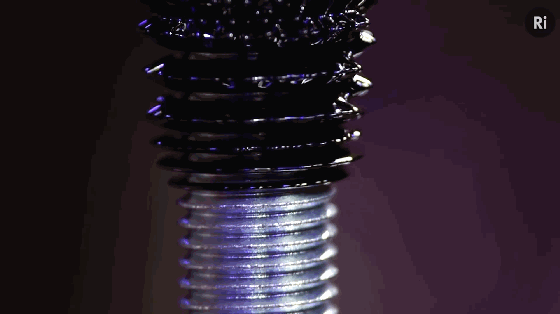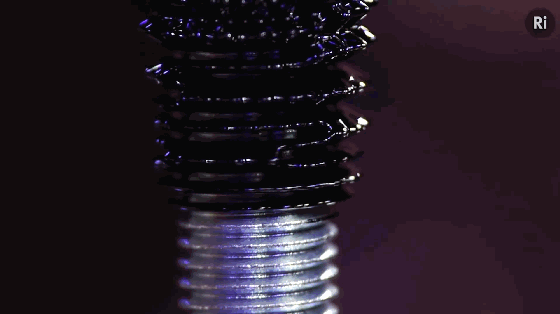
9. Metamaterials
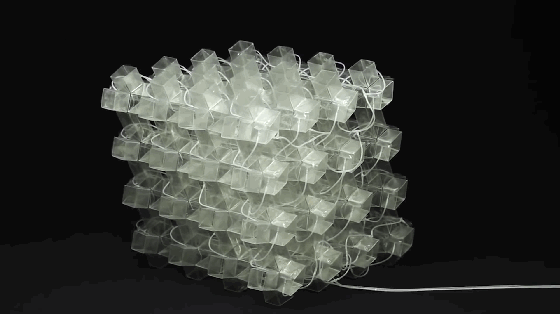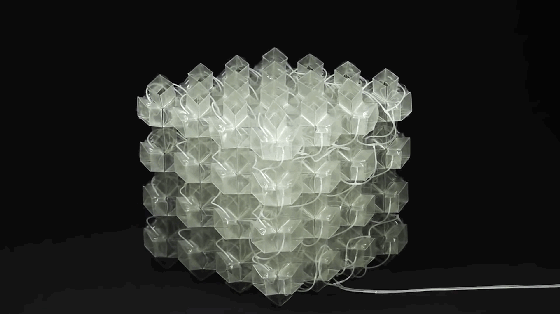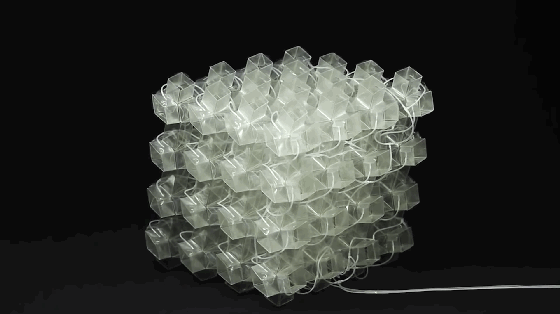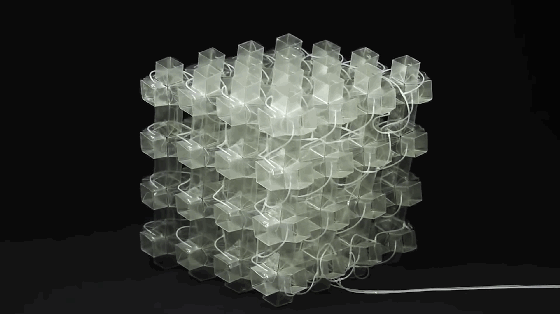
Metamaterials are a general term for a class of artificial materials. Its structure is similar to that of crystals composed of crystal cells. However, the “crystal cells” in metamaterials are larger basic units than atoms or molecules, and the overall structure is completely artificial. Therefore, its properties do not simply depend on its chemical composition, and its basic unit and arrangement structure are very important. The figure shows the conceptual model of programmable metamaterials produced by 3D printing.
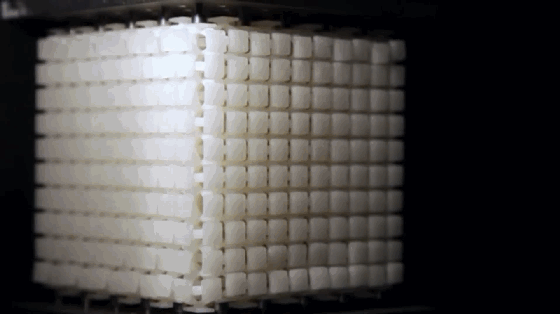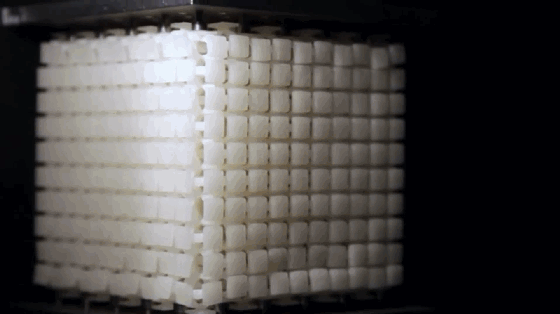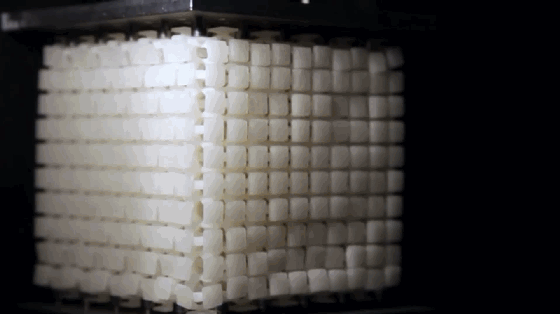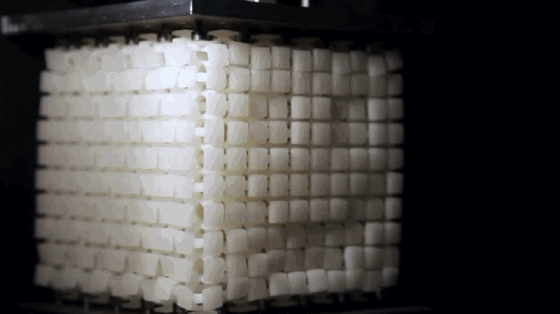
10. Non Newtonian fluid

Non Newtonian fluid refers to the fluid that does not meet Newton’s experimental law of viscosity. It widely exists in production, life and nature. The corn starch paste in the figure is one of the most common non-Newtonian fluids. It is “stronger when it is strong”. The greater the external force, the harder it will appear. Of course, there are many other kinds of non-Newtonian fluids with different properties.

Comments